Iran On The World Map: Unveiling Its Strategic Heart
Understanding the intricate tapestry of global geography often begins with pinpointing key nations and their unique positions. When we talk about "Iran on the map of the world," we're not just discussing a geographical location; we're delving into a country with a profound historical legacy, a strategic geopolitical role, and a rich cultural heritage that has shaped civilizations for millennia. Its placement at the nexus of the Middle East, South Asia, and Central Asia gives it an unparalleled significance, influencing trade, culture, and international relations throughout history and into the present day.
This article aims to explore the multifaceted aspects of Iran's presence on the global stage, from its precise geographical coordinates and extensive borders to its ancient past as Persia, its vibrant modern cities, and its pivotal role in contemporary geopolitics. By exploring Iran's location on the world map, we gain a deeper appreciation for its complex identity and its enduring impact on the world.
Table of Contents
- Where Exactly is Iran on the World Map?
- A Tapestry of Time: Iran's Ancient Roots and Enduring Legacy
- The Strategic Crossroads: Iran's Geopolitical Significance
- Navigating Iran's Diverse Landscape: Mountains, Deserts, and Coasts
- Major Cities and Cultural Hubs on the Map of Iran
- Iran's Provinces and Administrative Divisions
- Unveiling Iran's Rich Culture and Tourist Attractions
- Understanding Iran's Geopolitical Dynamics through its Map
Where Exactly is Iran on the World Map?
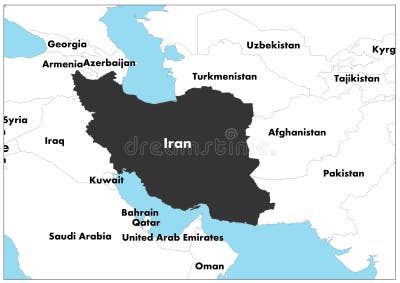
To truly grasp the significance of Iran, one must first locate it precisely on the world map. Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a prominent country in Western Asia. It occupies a critical position, bridging the Middle East and South Asia, and serves as an important geographic bridge connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa. When you look at Iran on a world wall map, it stands out as one of nearly 200 countries illustrated, often highlighted to show its unique political and physical features.
- Iran President
- Iran Queen
- What Does Benjamin Orrs Son Do
- Kohls Return Policy
- Iran Nuclear Deal Latest News
Geographical Coordinates and Borders
Iran's geographical coordinates place it roughly between latitudes 24° and 40° N, and longitudes 44° and 64° E. This vast expanse means it experiences a diverse range of climates and landscapes. The country shares extensive land borders with several nations, each contributing to its complex regional dynamics. To the west, Iran is bordered by Iraq and Turkey. To the north, it shares a border with Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan, as well as the vast Caspian Sea. To the east, its neighbors are Afghanistan and Pakistan. To the south, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman define its coastline, providing crucial access to international waters.
This intricate network of borders underscores Iran's role as a crossroads of civilizations and a historical hub for trade and cultural exchange. A detailed political map of Iran would clearly show these international borders, along with the national capital, Tehran, and various province capitals and major cities.
Size and Population at a Glance
Iran is not only strategically located but also impressively vast in size and population. It is the 18th largest country in the world, covering an area of approximately 1.65 million square kilometers. This makes it larger than many European nations combined and gives it a significant geographical footprint on the Asian continent. Its sheer size allows for a remarkable diversity of natural features, from towering mountains to expansive deserts and fertile plains.
- Iran Pornolar
- Iran Us Embassy
- Kings Theatre
- Irans Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei
- Cyrus Cylinder Iran
In terms of population, Iran is the 17th most populous country globally, with a population of around 83 million people. This makes it a significant demographic force in the region, following countries like Egypt and Turkey in regional population figures. This large and diverse population contributes to Iran's rich cultural tapestry and its dynamic internal landscape, influencing everything from its economy to its political structure.
A Tapestry of Time: Iran's Ancient Roots and Enduring Legacy
Beyond its contemporary geographical and demographic statistics, Iran's story is deeply rooted in antiquity. Historically known as Persia until 1935, Iran represents one of the world's oldest continuous civilizations with a documented history spanning over 7,000 years. This makes it a living testament to human endurance, innovation, and cultural evolution.
From Persia to the Islamic Republic
Archaeological evidence confirms human settlements in the region dating back to 10,000 BCE, with urban development emerging around 4000 BCE in areas like Susa and Sialk. These early settlements laid the groundwork for powerful empires that would shape the course of history. The Achaemenid Empire, for instance, with its ancient ceremonial capital at Persepolis, was one of the largest empires in ancient history, stretching from the Balkans to the Indus Valley. Learning about Iran's location on the world map inevitably connects us to these grand historical narratives.
The transition from the ancient Persian empires to the modern Islamic Republic of Iran reflects centuries of cultural, religious, and political transformations. While the name changed in 1935, the deep historical and cultural identity of Persia continues to resonate throughout the country. This long and complex history, including its culture, religion, and politics, is intricately linked to its geographical position, which has facilitated both invasions and cultural exchanges over millennia.
The Strategic Crossroads: Iran's Geopolitical Significance
Iran's location on the world map is not merely a point of interest for geographers; it is a fundamental factor in understanding global geopolitics. Occupying a strategic location bridging the Middle East and South Asia, Iran's central position has historically made it a hub for trade routes, including the ancient Silk Road, and a focal point for cultural diffusion. This historical role continues to define its contemporary strategic importance.
The country's access to both the Caspian Sea in the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in the south provides it with critical maritime routes. The Persian Gulf, in particular, is a vital artery for global oil shipments, making Iran a key player in international energy markets. This dual access to major waterways, combined with its extensive land borders, positions Iran as a gateway between different regions and continents.
Recent global events have further underscored Iran's geopolitical sensitivity. Reports of strikes and counter-strikes between nations like Israel and Iran, targeting military infrastructure or nuclear facilities, highlight the volatile nature of the region. Live air tracking maps, such as those from FlightRadar24, sometimes show "gaping holes" over areas like Israel, Iraq, Iran, and Ukraine, indicating zones of conflict or heightened security, with most air traffic rerouted. This illustrates how Iran's strategic position can become a flashpoint, impacting global stability and drawing the attention of major powers like Britain and the US. CNN, for example, has reported on and tracked where attacks are happening and which Iranian nuclear facilities have been targeted, further emphasizing the global focus on Iran's strategic importance.
Navigating Iran's Diverse Landscape: Mountains, Deserts, and Coasts
An exploration of Iran's map reveals a country of stunning geographical diversity. From towering mountain ranges to vast arid deserts and fertile coastal plains, Iran's topography is as varied as its history. This diverse landscape significantly influences its climate, population distribution, and economic activities.
The country is characterized by several major mountain ranges, including the Alborz Mountains in the north, home to Mount Damavand, the highest peak in Iran and the Middle East, and the Zagros Mountains, which stretch across its western and southwestern parts. These mountains play a crucial role in Iran's hydrology, trapping moisture and feeding rivers, while also creating distinct climatic zones. A topographic map of Iran would clearly show these majestic mountains in shaded relief, along with ocean depth in blue color gradient, providing a comprehensive physical overview.
Between these mountain ranges lie expansive desert basins, such as the Dasht-e Kavir (Great Salt Desert) and the Dasht-e Lut (Empty Desert), which are among the hottest and most arid places on Earth. These deserts, while challenging for human habitation, contribute to Iran's unique natural beauty and biodiversity. The interplay of mountains and deserts creates a fascinating mosaic of ecosystems across the country.
Key Waterways: Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf, and Gulf of Oman
Iran's geographical identity is heavily defined by its access to significant bodies of water. The Caspian Sea borders Iran to the north, representing the world's largest inland body of water. This connection provides Iran with access to Central Asian markets and natural resources, although its status as a sea or lake has led to complex international agreements among littoral states.
To the south, Iran's coastline stretches along the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. The Persian Gulf is a semi-enclosed sea that is crucial for global energy security due to its vast oil and natural gas reserves. The Strait of Hormuz, a narrow passage connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and then to the Arabian Sea, is one of the world's most critical chokepoints for oil transit. Iran's control over a significant portion of this strait gives it immense strategic leverage, making its southern maritime borders exceptionally important on the world map.
Major Cities and Cultural Hubs on the Map of Iran
An exploration of Iran's map would be incomplete without highlighting its vibrant and culturally rich cities. These urban centers showcase Iran's historical and contemporary significance, serving as economic, political, and cultural hubs. The capital city, Tehran, is a bustling metropolis that serves as the center of the economic and political map of Iran. It is the largest city in Iran and one of the largest in Western Asia, a sprawling urban area nestled at the foot of the Alborz Mountains.
Beyond Tehran, other significant cities dot the Iranian landscape, each with its own unique character and historical importance. These include:
- Isfahan: Renowned for its stunning Islamic architecture, beautiful bridges, and the UNESCO World Heritage site of Naqsh-e Jahan Square.
- Shiraz: Often called the city of poets, literature, and gardens, home to the tombs of Hafez and Sa'di, and close to the ancient ruins of Persepolis.
- Mashhad: The holiest city in Iran, a major pilgrimage site for Shia Muslims, housing the Imam Reza shrine.
- Tabriz: A historical capital and a major commercial hub, known for its grand bazaar and its rich Azerbaijani culture.
- Qom: Another significant religious center, particularly for Shia theological studies.
These cities, along with many others, are connected by an extensive network of main roads and railroads, as depicted on a detailed map of Iran. They serve as vital nodes for internal trade, administration, and cultural exchange, reflecting the diverse fabric of the nation.
Iran's Provinces and Administrative Divisions
To understand the internal structure of Iran, it's essential to look at its administrative divisions. Iran is divided into 31 provinces (ostanha), each with its own capital city. These provinces are further subdivided into counties (shahrestan), districts (bakhsh), and rural districts (dehestan). This system allows for decentralized governance and administration across the vast country.
Exploring Iran's map at a provincial level provides a more granular view of its regional variations in geography, climate, and population density. For instance, the northern provinces along the Caspian Sea are known for their lush, humid climate, while provinces in the central plateau are predominantly arid. Each province contributes to the overall identity of Iran, with distinct local cultures, traditions, and economic activities. Understanding these divisions helps in comprehending the complexities of Iran's internal politics and socio-economic landscape.
Unveiling Iran's Rich Culture and Tourist Attractions
Beyond its strategic location and historical depth, Iran offers a wealth of cultural experiences and tourist attractions. For those looking to explore this country, its map is a guide to ancient wonders, natural beauty, and vibrant modern life. From the ancient ruins of Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire, to the bustling bazaars of Tabriz and the serene gardens of Shiraz, Iran promises a journey through time and tradition.
Some of Iran's most famous travel destinations and attractions include:
- Persepolis: A UNESCO World Heritage site, offering a glimpse into the grandeur of the ancient Persian Empire.
- Naqsh-e Jahan Square (Isfahan): Another UNESCO site, featuring magnificent mosques, palaces, and a grand bazaar.
- Yazd: Known for its unique desert architecture, ancient windcatchers, and Zoroastrian heritage.
- Golestan Palace (Tehran): A masterpiece of the Qajar era, blending Persian and Western architectural styles.
- The Ancient City of Susa and Sialk: Archaeological sites providing insights into early urban development.
Visitors can also learn about Iran's official symbols, seal, and flag, which are integral to its national identity. Practical information like postal/area/zip codes and time zones are also essential for anyone planning to explore this fascinating country. While Google Maps can help find local businesses and get driving directions, truly understanding Iran on the map of the world involves appreciating its deep cultural layers.
Understanding Iran's Geopolitical Dynamics through its Map
The geopolitical landscape of the Middle East and beyond is inextricably linked to Iran's position on the world map. Its borders with Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, coupled with its access to the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf, place it at the heart of regional power dynamics. This strategic location has made Iran a key player in various regional conflicts and international diplomatic efforts.
The ongoing discussions around Iran's nuclear program, its role in regional proxy conflicts, and its relationships with global powers are all framed by its geographical realities. The ability to project influence across land and sea, control vital maritime routes, and serve as a bridge between different cultural and political spheres gives Iran a unique and often challenging role on the global stage. Understanding where Iran is located, what its capital and largest city are, and how it is bordered by other countries and seas provides the fundamental context for comprehending its complex foreign policy and domestic challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring "Iran on the map of the world" reveals far more than just geographical coordinates. It unveils a nation with an ancient soul, a strategic mind, and a vibrant cultural heart. From its historical roots as Persia, dating back over 7,000 years, to its modern identity as the Islamic Republic of Iran, the country's location has consistently placed it at the crossroads of civilizations, trade, and geopolitical influence. Its vast size, diverse landscapes, and access to crucial waterways like the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf underscore its enduring importance.
Whether you are interested in its rich history, its stunning natural features, its bustling cities like Tehran, or its pivotal role in international affairs, Iran's position on the world map is central to understanding its past, present, and future. We encourage you to delve deeper into the fascinating story of this ancient land. What aspects of Iran's geography or history do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore our other articles to continue your journey through the world's most captivating nations.
Iran World Black Map White Background Classic Style Stock Illustration

Israel Vs Iran - Brilliant Maps

How conflict between Israel and Iran has unfolded over four days