Iran's Population In 2024: What The Latest Numbers Reveal
The demographic landscape of any nation is a dynamic tapestry woven from birth rates, mortality, migration, and socio-economic shifts. For Iran, a country with a rich history and a pivotal role in the Middle East, understanding its population trends is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and anyone interested in regional developments. As we delve into the population of Iran 2024 estimate, we uncover not just numbers, but insights into the nation's present trajectory and future challenges.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Iran's demographic situation, focusing specifically on the latest estimates for 2024. We will explore the methodologies behind these figures, highlight the key data points, and discuss the broader implications of these trends. From understanding the nuances of de facto population counts to examining the factors that shape Iran's growth, we invite you to join us on a journey to decode the fascinating story told by the numbers.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Population of Iran 2024 Estimate: The Basics
- Key Figures: Iran's Population Growth in Recent Years
- The 2024 Estimates: A Closer Look at the Numbers
- Decoding the Discrepancies: Why Estimates Vary
- Beyond the Numbers: Factors Influencing Iran's Demographics
- The Future Outlook: Projections for Iran's Population Beyond 2024
- Socio-Economic Implications of Iran's Population Trends
- Navigating Data: The Importance of Reliable Sources
- Conclusion: What the Population of Iran 2024 Estimate Means for the Future
Understanding the Population of Iran 2024 Estimate: The Basics
Before diving into the specific figures for the population of Iran 2024 estimate, it's essential to grasp the fundamental principles that underpin demographic calculations. Population statistics are not simply a headcount; they are the result of meticulous methodologies designed to capture a snapshot of a nation's residents at a particular moment in time. Two key concepts are central to understanding these figures: the de facto definition of population and the use of midyear estimates.De Facto Population: Who is Counted?
When we talk about the total population for Iran, or any country for that matter, the figures are typically based on the "de facto" definition of population. This approach counts all residents who are physically present within the country's borders at the time of the census or estimate, regardless of their legal status or citizenship. This means that both citizens and non-citizens, including temporary residents, migrant workers, refugees, and even tourists present on the specific date, are included in the count. The de facto method contrasts with the "de jure" method, which counts individuals based on their usual residence or legal affiliation, regardless of where they are physically located on the day of the count. For a country like Iran, which hosts a significant number of refugees and has a dynamic cross-border movement, the de facto definition provides a more immediate and practical measure of the population that needs to be supported by public services and infrastructure. It gives a clearer picture of the actual demand on resources within the country's geographical boundaries.Midyear Estimates: A Standard Approach
Another crucial aspect of understanding population data is the concept of midyear estimates. The values shown for Iran's population, including the projections for 2024, are typically midyear estimates. This means the population figure represents the estimated number of people residing in the country as of July 1st of a given year. Why July 1st? This midyear point is chosen because it effectively balances out seasonal variations in population that might occur due to factors like tourism, seasonal migration, or even academic calendars. By taking the middle of the year, demographers aim to provide a more stable and representative figure that can be reliably compared across different years and between different countries. It helps to smooth out any temporary fluctuations, offering a more robust baseline for demographic analysis and future projections. These estimates are often derived from the latest census figures, adjusted by tracking births, deaths, and net migration since the last full census.Key Figures: Iran's Population Growth in Recent Years
To appreciate the 2024 estimates, it's helpful to look at Iran's recent demographic trajectory. The country has experienced consistent, albeit moderate, growth over the past few years. This steady increase provides context for the current projections and helps us understand the underlying momentum of Iran's population dynamics. According to the provided data, Iran's population has shown a consistent growth rate of 1.21% year-on-year:- Total population for Iran in 2022 was 89,524,246, marking a 1.21% increase from 2021.
- Building on this, the total population for Iran in 2023 reached 90,608,707, which was again a 1.21% increase from 2022.
The 2024 Estimates: A Closer Look at the Numbers
As we approach the heart of our discussion, it's important to note that population estimates can sometimes vary depending on the source and the methodology employed. For the population of Iran 2024, we have two prominent figures from reputable organizations: the United Nations and Trading Economics. Both provide valuable insights, though their numbers present a slight difference, which we will explore further.United Nations Projections for Iran's Population 2024
The United Nations is widely regarded as a leading authority in global demographic data and projections. Their estimates are based on comprehensive analyses of census data, vital statistics (births and deaths), and international migration patterns, often employing sophisticated demographic models. According to the latest United Nations estimates for 2024, the population of Iran is projected at 91,567,738 as of July 1st. This figure, often rounded to 91.57 million people, reflects the UN's assessment of Iran's ongoing demographic trajectory, taking into account recent growth rates and anticipated future trends in fertility, mortality, and migration. This specific number is a key reference point when discussing the estimated population of Iran for 2024, providing a benchmark from a globally recognized institution.Trading Economics' Perspective on Iran's Population 2024
Trading Economics is another respected platform that compiles and projects economic and demographic data from various official sources, including national statistical offices and international organizations. Their figures are often based on the latest census data combined with their own projections. In contrast to the UN's figure, Trading Economics estimated the total population in Iran at 86.0 million people in 2024, according to their latest census figures and projections. This is a noticeable difference compared to the UN's estimate of 91.57 million. This discrepancy underscores the complexities inherent in demographic forecasting and the various factors that can lead to different outcomes, even when using reliable data. Understanding these differences is crucial for a nuanced view of Iran's demographic outlook for 2024.Decoding the Discrepancies: Why Estimates Vary
The existence of different figures for the population of Iran 2024, even from highly credible sources like the United Nations and Trading Economics, is not uncommon in demography. Rather than signaling an error, it highlights the inherent challenges and complexities involved in accurately measuring and projecting human populations. Several factors contribute to these variations: * **Base Year and Latest Census Data:** Different organizations might be working off slightly different base years for their projections, or they might have access to the most recent census data at varying times. If one organization's projection is based on a census from, say, 2016, while another has incorporated more recent preliminary data or a 2020 census, their starting points for projection will differ. * **Methodology and Assumptions:** Demographic projections rely on assumptions about future trends in fertility rates (births per woman), mortality rates (death rates), and international migration (both immigration and emigration). These assumptions can vary significantly between models. For instance, one model might assume a faster decline in fertility or a higher rate of emigration due to socio-economic factors, leading to a lower projected population. Conversely, more optimistic assumptions could lead to higher figures. * **Data Collection Challenges:** In any country, especially one with diverse geographical regions and potentially complex socio-political dynamics, collecting comprehensive and accurate demographic data can be challenging. Issues like undercounting in remote areas, difficulties in tracking internal migration, or incomplete registration of births and deaths can introduce inaccuracies into the base data used for projections. * **Inclusion of Specific Groups:** While both sources likely use a de facto definition, there might be subtle differences in how certain transient or hard-to-count populations (e.g., undocumented migrants, seasonal workers, or specific ethnic groups) are estimated or included in the overall count. * **Purpose of the Estimate:** Sometimes, the purpose for which an estimate is generated can subtly influence the methodology. For instance, an economic forecasting firm might prioritize economic indicators that influence migration, while a humanitarian organization might focus more on vulnerable populations. These factors illustrate that population estimates are not absolute facts but rather informed projections based on the best available data and sophisticated models. When evaluating the population of Iran 2024, it's wise to consider the range of estimates and understand the underlying assumptions that drive them. This critical approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the demographic landscape.Beyond the Numbers: Factors Influencing Iran's Demographics
The numbers for the population of Iran 2024 estimate are not isolated figures; they are the culmination of complex socio-economic, cultural, and political factors. Understanding these underlying drivers provides deeper insight into Iran's demographic trajectory. * **Fertility Rates:** Historically, Iran experienced a rapid decline in fertility rates from very high levels in the 1980s to below replacement levels in the 2000s. This decline was influenced by factors such as increased female education, urbanization, access to family planning, and changing societal norms. While there have been government efforts in recent years to encourage higher birth rates, the long-term trend of lower fertility continues to shape the age structure and future growth potential. * **Mortality Rates and Healthcare:** Improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and living standards have led to a significant decrease in mortality rates and an increase in life expectancy in Iran. This contributes to population growth by ensuring more people live longer. However, challenges related to access to advanced medical care, environmental pollution, and lifestyle diseases remain. * **International Migration:** Migration plays a crucial role. Iran has historically been a host country for millions of Afghan refugees, and their presence significantly impacts the de facto population count. Conversely, economic pressures and social factors can lead to emigration, particularly among educated youth and skilled professionals, often referred to as "brain drain." The net effect of these movements significantly influences the overall population size. * **Urbanization:** Iran is a highly urbanized country, with a majority of its population residing in cities. Urbanization often correlates with lower fertility rates, as city dwellers tend to have smaller families due to higher living costs, career aspirations, and access to education and family planning services. The growth of major cities like Tehran, Mashhad, and Isfahan continues to shape internal migration patterns. * **Socio-Economic Conditions:** Economic sanctions, inflation, and unemployment can profoundly impact demographic decisions. Economic uncertainty might lead couples to postpone marriage and childbearing, or it might drive individuals to seek opportunities abroad. Conversely, periods of economic stability could potentially encourage larger families. * **Government Policies:** The Iranian government has, at various times, implemented policies aimed at influencing population growth. In the past, family planning initiatives were promoted to curb rapid growth. More recently, concerns about an aging population and a declining birth rate have led to policies encouraging larger families, including financial incentives and restrictions on family planning services. The effectiveness of these policies in altering long-term trends is a subject of ongoing debate and observation. * **Education and Women's Empowerment:** Increased access to education for women has been a major factor in demographic shifts globally, and Iran is no exception. Educated women tend to marry later, pursue careers, and have fewer children. This empowerment, while beneficial for societal development, has a direct impact on fertility rates. These interwoven factors create a complex demographic picture for Iran, one that extends far beyond the simple numbers of the population of Iran 2024 estimate. They highlight the intricate relationship between human lives and the broader societal context.The Future Outlook: Projections for Iran's Population Beyond 2024
While our primary focus is the population of Iran 2024 estimate, it's also insightful to look slightly ahead to understand the projected trajectory. Demographic trends often have a certain momentum, and understanding future projections helps in long-term planning. According to the United Nations, the population of Iran is projected to reach 92,417,681, or 92.42 million, as of July 1, 2025. This projection suggests a continued, albeit perhaps slightly slower, growth rate compared to the previous years' 1.21%. The increase from the 2024 UN estimate of 91.57 million to 92.42 million in 2025 represents an addition of approximately 850,000 people. This forward projection is critical for national planning. A continuously growing population, even at a slower pace, means that the demand for resources, infrastructure, and services will continue to increase. Policymakers must consider these future numbers when formulating strategies for urban development, employment generation, healthcare provision, and educational facilities. The slight moderation in the growth rate might indicate a maturing demographic profile, where the proportion of younger age groups might stabilize or even begin to shrink relative to older age groups, signaling a demographic transition. This shift has its own set of challenges and opportunities that Iran will need to navigate in the coming decades.Socio-Economic Implications of Iran's Population Trends
The numbers behind the population of Iran 2024 estimate and its future projections carry profound socio-economic implications. A nation's demographic structure directly influences its economy, social services, and political stability. * **Labor Force and Employment:** A growing population, particularly if it's young, implies an expanding labor force. This can be a demographic dividend if there are sufficient job opportunities. However, if job creation lags behind population growth, it can lead to high unemployment rates, particularly among youth, which can foster social discontent and economic instability. Iran faces the challenge of absorbing its relatively young population into productive employment. * **Education and Healthcare Demands:** More people mean a greater demand for public services. The education system needs to expand to accommodate new generations, requiring more schools, teachers, and resources. Similarly, the healthcare system faces increased pressure to provide medical facilities, personnel, and public health initiatives. An aging population, which Iran is also starting to experience due to declining birth rates and increased life expectancy, will place different demands on healthcare, focusing more on chronic diseases and geriatric care. * **Infrastructure and Urban Planning:** Continuous population growth, especially in urban centers, necessitates massive investments in infrastructure. This includes housing, transportation networks (roads, public transit), water and sanitation systems, and energy supply. Rapid urbanization without adequate planning can lead to overcrowding, pollution, and a decline in the quality of life. * **Resource Management:** A larger population consumes more natural resources, including water, food, and energy. For a country like Iran, which faces significant water scarcity issues, population growth exacerbates existing environmental challenges and necessitates sustainable resource management strategies. Food security also becomes a more pressing concern. * **Social Cohesion and Welfare:** Demographic shifts can impact social cohesion. A large youth bulge, if not adequately integrated into society and the economy, can be a source of social unrest. Conversely, an aging population requires robust social welfare systems, including pensions and elder care, which can strain public finances. The balance between different age groups and their needs is critical for social harmony. * **Economic Growth Potential:** While a large population can provide a substantial domestic market and a strong labor force, its contribution to economic growth depends on productivity, education levels, and the overall economic environment. Investing in human capital – education, skills training, and health – is paramount to harnessing the potential of a growing population. The estimated population of Iran for 2024, therefore, is not just a static figure but a dynamic indicator of the pressures and opportunities that lie ahead for the nation. Understanding these implications is vital for strategic national development.Navigating Data: The Importance of Reliable Sources
In an age of information overload, the ability to discern reliable data from misinformation is more crucial than ever. When researching sensitive topics like the population of Iran 2024 estimate, relying on credible and authoritative sources is paramount. The data presented in this article primarily draws from two highly respected entities in demographic and economic data: the United Nations and Trading Economics. * **United Nations (UN):** The UN, through its various departments and agencies (such as the Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division), is a global leader in collecting, analyzing, and disseminating demographic statistics. Their projections are based on rigorous methodologies, extensive data collection from member states, and peer-reviewed research. They provide standardized data that allows for international comparisons, making them a cornerstone for global demographic studies. * **Trading Economics:** This platform aggregates official statistics from national and international sources, providing a comprehensive database of economic indicators, including population data. While they compile data from various sources, their strength lies in presenting a wide array of statistics in an accessible format, often with their own projections based on these official figures. When encountering population statistics, it's always advisable to: 1. **Check the Source:** Is the information coming from a recognized statistical agency, an academic institution, or a reputable international organization? 2. **Understand the Methodology:** Are the figures based on a census, a survey, or a projection? What definition of population (de facto/de jure) is used? What is the reference date (e.g., midyear)? 3. **Look for Consistency:** While minor discrepancies are normal, significant differences between sources warrant further investigation into their methodologies or base data. 4. **Consider the Date of Publication:** Demographic data can change rapidly. Ensure you are looking at the most current estimates and projections. By adhering to these principles, individuals and researchers can confidently navigate the vast landscape of demographic data and gain accurate insights into the population of Iran 2024 and beyond.Conclusion: What the Population of Iran 2024 Estimate Means for the Future
The journey through Iran's demographic landscape, culminating in the population of Iran 2024 estimate, reveals a nation undergoing continuous evolution. With figures from the United Nations projecting 91.57 million people as of July 1, 2024, and a consistent growth rate observed in previous years, Iran's population continues its upward trajectory, albeit with varying estimates from different reputable sources like Trading Economics. These numbers are not just statistics; they are reflections of human lives, societal changes, and future aspirations. The insights gained from understanding the de facto population definition, midyear estimates, and the factors influencing demographic shifts — from fertility rates to migration and government policies — highlight the complexity of population dynamics. The socio-economic implications are vast, touching upon labor markets, infrastructure, resource management, and the overall well-being of the nation. As Iran looks towards 2025 with a projected population of 92.42 million, the need for strategic planning and sustainable development becomes ever more critical. We hope this comprehensive article has provided you with valuable insights into the estimated population of Iran for 2024 and the broader demographic trends shaping the country. Understanding these figures is vital for informed discussions about Iran's future. What are your thoughts on Iran's population trends? Do you have any questions about the data or its implications? Share your comments below! If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might be interested, and explore our other articles for more in-depth analyses of global demographic and economic trends.- Stephen Blosil
- Gooya News Persian News
- Ben Napier Next Project
- Mm2 Values Trading
- Mr Bean Death News

World population could peak at 8.5 billion people by the 2050s, study
Population Year 2022 - Worldmapper
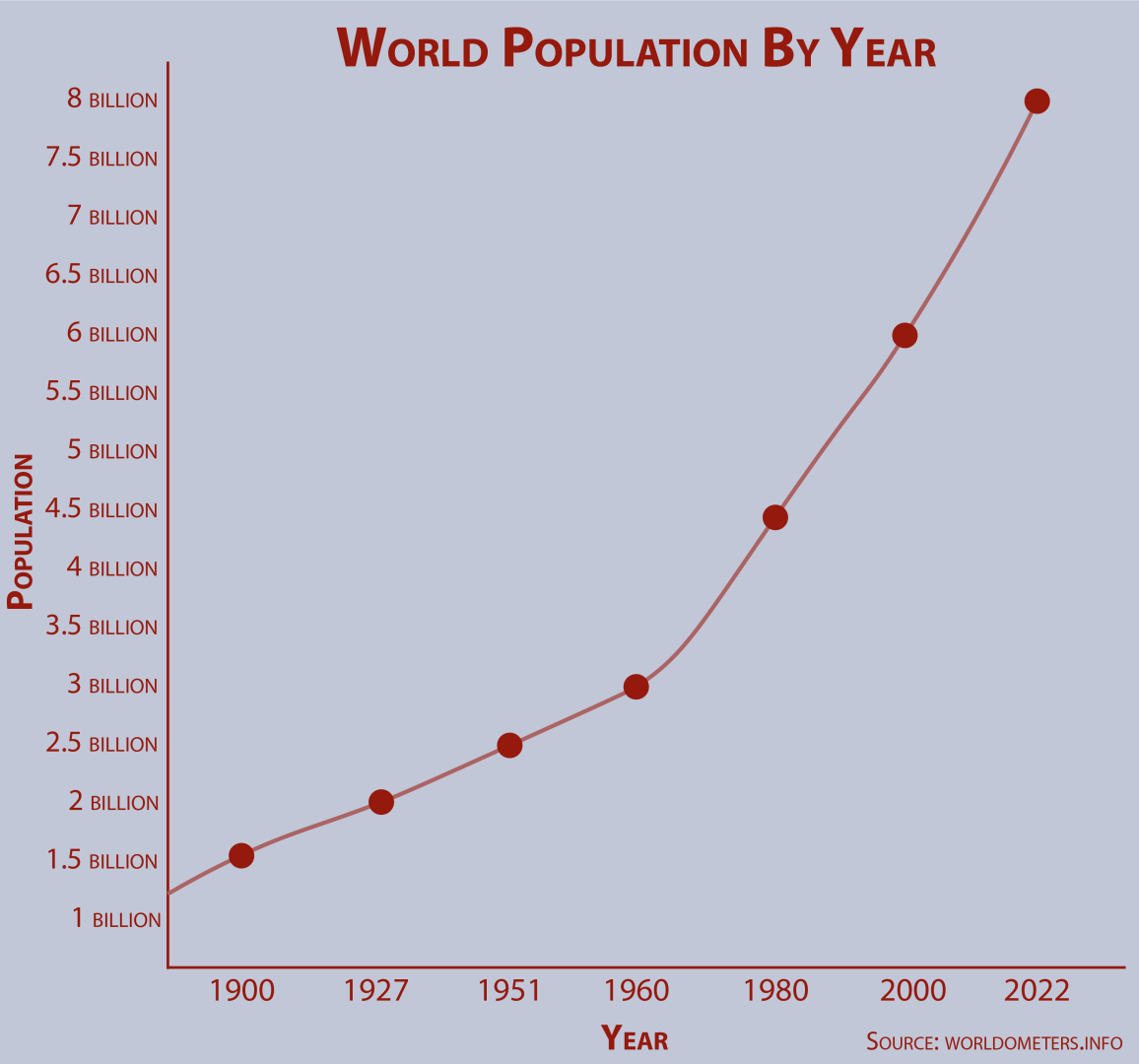
Global population reaches eight billion – The Reflector