Iran's Demographic Crossroads: Unpacking The Population Of Iran Mid 2025
The demographic landscape of nations is a dynamic tapestry, constantly shifting under the influence of births, deaths, and migrations. For Iran, a country with a rich history and a pivotal role in the Middle East, understanding its population dynamics is crucial for economic planning, social policy, and environmental sustainability. As we approach mid-2025, the latest projections offer a fascinating glimpse into the numerical heartbeat of this ancient land, revealing trends that will shape its future for decades to come.
This article delves deep into the projected population of Iran mid 2025, examining the key statistics, underlying demographic trends, and what these figures signify for the nation's trajectory. From growth rates to median age, urbanization to fertility, we will explore the multifaceted aspects of Iran's demographic profile, providing a comprehensive and insightful overview for general readers interested in the future of this significant nation.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Population of Iran Mid 2025: The Core Numbers
- A Historical Glimpse: Iran's Population Trajectory
- Decoding Growth Rates and Future Projections
- The Shifting Sands of Age: Median Age and Population Structure
- Fertility, Life Expectancy, and Mortality Trends
- Urbanization and Population Density: Where Iranians Live
- Global Context: Iran's Place in the World Population
- The Future Outlook: Beyond Mid-2025
Understanding the Population of Iran Mid 2025: The Core Numbers
As we navigate towards the middle of 2025, the most consistent and widely cited projections for Iran's populace point to a significant milestone. Specifically, the population of Iran mid 2025 is estimated at a robust 92,417,681 people, or approximately 92.42 million, as of July 1st. This figure represents a crucial snapshot in the nation's demographic evolution, offering insights into its current trajectory and future potential. To put this into a global perspective, Iran's population is equivalent to about 1.12% of the total world population, making it a moderately populous nation with a notable share of the global demographic pie.
- Jessica Sodi Age
- Where Is Iran Located In The World
- Iran Population Latest Statistics
- Meryl Streep Children
- Gabrielle Anwar Birth Year
It's important to acknowledge that demographic projections, by their nature, can vary slightly depending on the data source and methodology employed. For instance, some analyses project the current population of the Islamic Republic of Iran at 92,200,525 as of March 31, 2025, based on Worldometer's elaboration of the latest United Nations data. Another projection suggests a total current population for Iran in 2025 of 90,410,659, indicating a 0.67% increase from 2024. This variation underscores the dynamic nature of population estimation and the importance of referring to specific dates and methodologies. However, for the purpose of understanding the "mid-2025" scenario, the 92.42 million figure for July 1st stands out as the most precise estimate for our focus period. For comparison, the total population in Iran was projected at 91,567,738, or 91.57 million people, for the year 2024, indicating a steady, albeit moderating, growth into 2025.
A Historical Glimpse: Iran's Population Trajectory
To truly grasp the significance of the population of Iran mid 2025, it's essential to look back at the nation's demographic journey. Iran has experienced dramatic population shifts over the past several decades, moving from a relatively smaller base to its current substantial size. In the 1960s, Iran's population was significantly lower, but it underwent periods of rapid growth, particularly following the 1979 revolution and during the post-war reconstruction era. This rapid expansion was fueled by high birth rates and improving healthcare, which reduced mortality rates.
Visualizing this growth through population data graphs reveals a steep upward curve from 1960 onwards. These graphs, often depicting total population alongside birth and death rates, life expectancy, and median age, illustrate a consistent increase over the decades, reaching figures that now approach the 100 million mark. While the initial decades saw explosive growth, more recent trends indicate a slowdown. This deceleration is a natural part of demographic transition, as societies become more urbanized, educated, and economically developed. Understanding this historical context provides a vital backdrop for interpreting the current and future projections for Iran's population, highlighting a nation that has matured demographically and is now entering a new phase of its population story.
- Donald Trump Jewish
- Pizzas By Sadik
- Mr Bean Death News
- Ali Khamenei Date Of Birth
- Karen Carpenters Final Words
Decoding Growth Rates and Future Projections
The growth rate is a critical indicator of a nation's demographic vitality, and for Iran, it tells a story of moderation. While the country saw significant population increases in previous decades, the rate of growth has been decelerating. For 2025, projections indicate a modest increase. For instance, one data point suggests a 0.67% increase from 2024 to 2025, with the total current population for Iran in 2025 reaching 90,410,659. However, when comparing the 2024 projection of 91.57 million to the mid-2025 projection of 92.42 million, we observe a growth of approximately 0.85 million people over the year, which translates to a growth rate of about 0.93%.
Looking further into the future, studies project that Iran's rate of population growth will continue to slow until it stabilizes above 100 million by 2050. This long-term trend suggests that Iran, much like other nations that have undergone similar demographic transitions, is approaching its "population zenith." Countries such as Brazil, Turkey, and Vietnam are also expected to reach their population peaks between 2025 and 2054. These nations, including Iran, may experience moderate growth—around 5.3%—before eventually entering a downward trend. This projected trajectory has profound implications for national planning, resource allocation, and economic development, as a slower-growing or even declining population presents different challenges and opportunities compared to one experiencing rapid expansion. The moderation of Iran's growth rate is a key factor shaping the future beyond the immediate population of Iran mid 2025.
The Shifting Sands of Age: Median Age and Population Structure
Beyond mere numbers, the age structure of a population offers profound insights into its societal dynamics and future potential. Iran has undergone a remarkable demographic transformation in this regard. In 2012, half of Iran's population was under 35 years old, indicating a significantly youthful demographic. This "youth bulge" presented both opportunities and challenges, with a large cohort entering working age, but also requiring substantial investment in education and job creation.
Fast forward to January 2025, and the average age of the Iranian population is projected to be 32 years. While still relatively young compared to many developed nations, this figure signifies a notable shift from the 2012 statistic. The median age, which divides the population into two equal halves, is also a crucial metric for understanding the population structure in mid-2025. As the average age increases, it suggests a maturing population, with a larger proportion of adults and a potentially smaller proportion of very young dependents. This demographic aging, though gradual, will influence everything from healthcare demands to pension systems and labor market dynamics, making it a central consideration for long-term policy planning.
Youth Bulge to Demographic Dividend?
The transition from a pronounced youth bulge to a maturing population brings with it the potential for a "demographic dividend." This phenomenon occurs when a country's working-age population grows larger relative to its dependent population (children and the elderly), leading to a period of accelerated economic growth. With an average age of 32 in early 2025, Iran is well-positioned to capitalize on this dividend, provided there are sufficient opportunities for education, employment, and economic participation for its large working-age cohort. However, if these opportunities are not adequately met, a large, underemployed young adult population can instead become a source of social and economic strain. The ability of Iran to harness this demographic window will largely determine its economic trajectory in the coming decades, making the median age a critical factor influencing the implications of the population of Iran mid 2025.
Fertility, Life Expectancy, and Mortality Trends
The fundamental drivers of population change are births, deaths, and migration. In Iran, the interplay of total fertility rate (TFR), life expectancy, and mortality rates has significantly shaped its demographic profile. While specific TFR figures for mid-2025 are not provided, the general trend of slowing population growth strongly implies a declining fertility rate. Many nations undergoing demographic transition experience a sharp drop in TFR as education levels rise, urbanization increases, and access to family planning improves. This decline means fewer births, directly impacting the future size and age structure of the population.
Conversely, life expectancy and mortality rates in 2025 are crucial for understanding how long Iranians are living and how quickly the population is being replenished. Improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and living standards typically lead to increased life expectancy and lower death rates. Population data graphs often illustrate these trends, showing declining birth rates alongside decreasing death rates, leading to a period of sustained growth before stabilization. The balance between these two forces—fewer births and longer lives—is what ultimately determines the pace of population change and contributes significantly to the projected population of Iran mid 2025.
The Role of Social Policies on Demographics
Government policies play a pivotal role in influencing demographic trends, particularly in areas like fertility and life expectancy. Historically, Iran has experienced shifts in its population policies, from encouraging large families in some periods to promoting family planning in others. Such policies, alongside investments in public health infrastructure, access to education, and economic opportunities for women, can profoundly impact a nation's total fertility rate. Similarly, advancements in healthcare systems, disease prevention programs, and social welfare initiatives directly contribute to improvements in life expectancy and reductions in infant and child mortality rates. Therefore, understanding the current demographic landscape, including the population of Iran mid 2025, necessitates an appreciation for the long-term effects of past and present social policies on the lives and choices of its citizens.
Urbanization and Population Density: Where Iranians Live
Beyond the total count, how a population is distributed geographically is equally important. Urbanization and population density are key aspects of Iran's demographic profile. Over recent decades, Iran has experienced significant internal migration, with a growing proportion of its population moving from rural areas to urban centers. This trend is common globally, driven by the pursuit of better economic opportunities, education, and access to services. As a result, Iran's major cities have expanded rapidly, becoming hubs of economic activity and cultural life. Population data often includes metrics on urbanization, illustrating the percentage of the population residing in urban areas, a figure that continues to climb for Iran.
Population density, which measures the number of people per unit of area, also provides critical insights. While Iran is a large country, much of its land is arid or mountainous, meaning that its population is concentrated in specific regions, particularly along the Caspian Sea coast, in the central plateau cities like Tehran, Isfahan, and Shiraz, and in the northwest. This concentration leads to high population densities in urban areas, placing pressure on infrastructure, housing, and resources. The ongoing trend of urbanization means that an even greater proportion of the population of Iran mid 2025 will reside in these already densely populated urban environments, bringing both economic dynamism and significant planning challenges.
Challenges of Rapid Urbanization
While urbanization often correlates with economic development, rapid and unplanned growth can lead to a myriad of challenges. For Iran, the increasing concentration of its population in urban centers necessitates robust planning for infrastructure development, including transportation, water, and energy. Housing affordability, waste management, and environmental pollution also become pressing concerns in densely populated cities. Moreover, the disparity between urban and rural areas can widen, leading to social inequalities. Addressing these challenges requires strategic urban planning, sustainable resource management, and equitable distribution of opportunities to ensure that the benefits of urbanization are shared across the entire population. The continued growth of urban centers will be a defining feature of the Iranian demographic landscape well beyond the immediate population of Iran mid 2025.
Global Context: Iran's Place in the World Population
Understanding the population of Iran mid 2025 gains further perspective when viewed within the broader global demographic landscape. The world population itself is a dynamic entity, having reached a significant milestone of 8 billion people on November 15, 2022, according to the United Nations. Iran's projected population of 92.42 million for mid-2025 means it accounts for approximately 1.12% of this vast global total. This places Iran among the more populous nations, though far from the top tier of countries like China or India.
Interestingly, Iran is also identified as one of the countries "approaching peak" in terms of population growth. Along with nations like Brazil, Turkey, and Vietnam, Iran is expected to reach its population zenith—the point at which its population growth rate begins to decline—sometime between 2025 and 2054. This puts Iran in a unique demographic cohort, distinct from countries experiencing steep population declines (like Lithuania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Albania) or those still experiencing rapid growth. This global comparison highlights that Iran's demographic journey is part of a larger, interconnected worldwide trend, where different regions and nations are at various stages of their demographic transition. Furthermore, considering Iran's position in the Middle East, its population trends are significant for regional stability and development, as it is one of the most populous countries in the area.
The Interconnectedness of Global Demographics
Demographic trends are rarely isolated phenomena; they are often influenced by global forces. Economic globalization, technological advancements, and even climate change can impact birth rates, migration patterns, and life expectancy across borders. For Iran, its demographic future, including the precise figures for the population of Iran mid 2025, is not solely determined by internal factors but also by its engagement with the wider world. International migration, for instance, can significantly alter population figures, though the provided data does not detail specific immigration trends for Iran. Global health crises, economic sanctions, or geopolitical shifts can also have ripple effects on a nation's demographic trajectory. Therefore, analyzing Iran's population requires an understanding of its place within the intricate web of global demographics, recognizing that its story is part of a larger human narrative.
The Future Outlook: Beyond Mid-2025
As we project beyond the immediate snapshot of the population of Iran mid 2025, the long-term demographic trends paint a clear picture of a nation undergoing significant transformation. Studies consistently project that Iran's population growth rate will continue to slow, eventually stabilizing above 100 million by 2050. This means that while the population will still grow, the pace of that growth will diminish considerably over the next few decades. This trajectory positions Iran among countries that will experience moderate growth before potentially entering a phase of decline after reaching their population peak, likely between 2025 and 2054.
The implications of this future outlook are profound. A stabilizing or eventually declining population will reshape Iran's economy, labor market, and social structures. It will necessitate adjustments in areas such as healthcare provision for an aging populace, pension systems, and educational planning. While a larger population can bring economic benefits through a larger workforce and consumer base, a more mature demographic structure with slower growth also presents opportunities for higher per capita income and better resource management. The journey from rapid expansion to demographic maturity is a complex one, and how Iran navigates these shifts will define its socio-economic landscape for the remainder of the 21st century. The data from mid-2025 serves as a crucial waypoint in this ongoing demographic evolution, offering a clear indication of the path ahead.
Conclusion
The demographic landscape of Iran in mid-2

World population could peak at 8.5 billion people by the 2050s, study
Population Year 2022 - Worldmapper
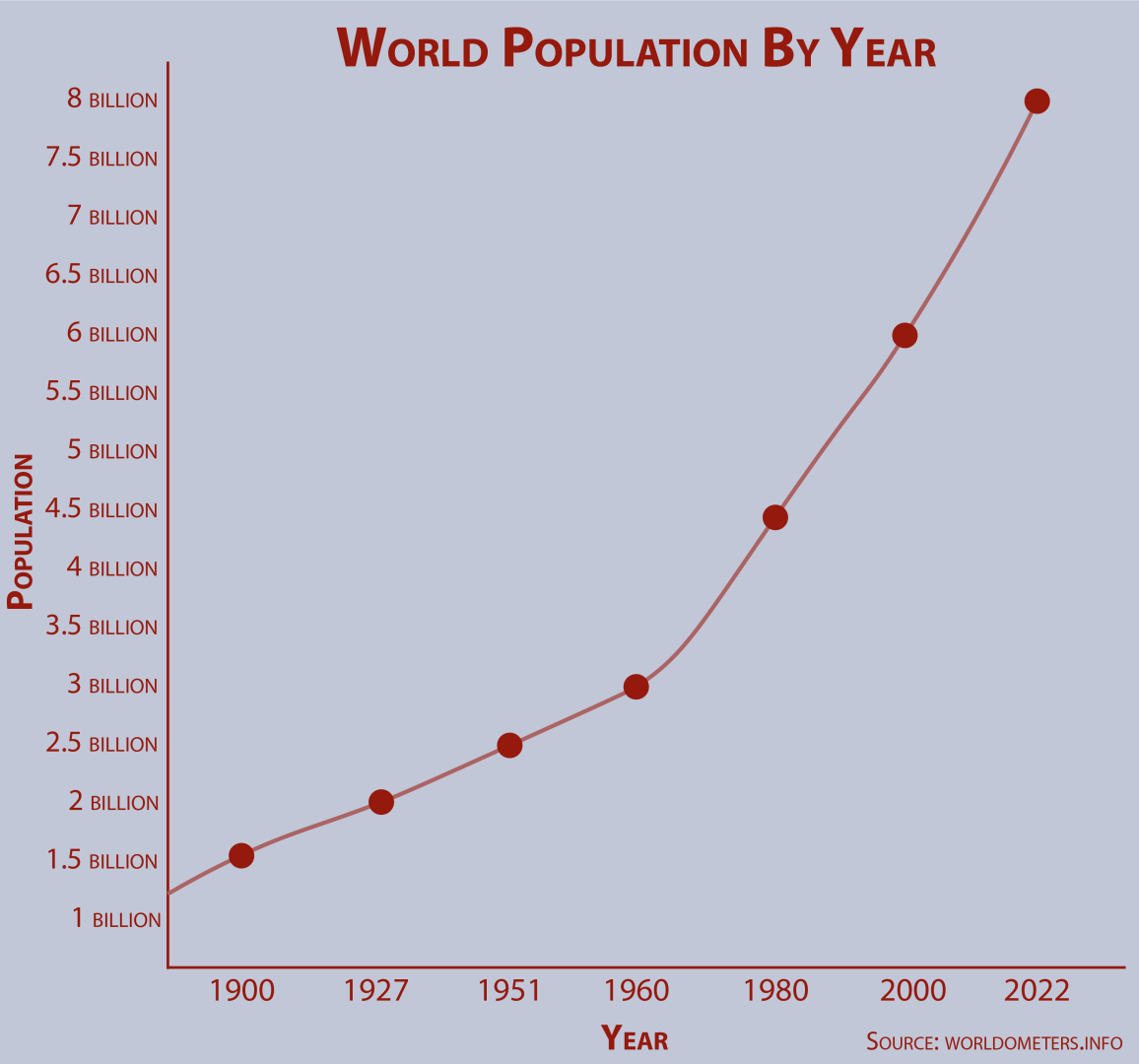
Global population reaches eight billion – The Reflector