Iran's Population Density: Unpacking The Numbers And Their Impact
Iran, a nation steeped in ancient history and rich culture, is also a country undergoing significant demographic shifts. Understanding the "population density of Iran" is not merely an academic exercise; it's a crucial lens through which we can examine the country's development, resource management, and future trajectory. From sprawling urban centers to vast, sparsely populated deserts, the distribution of Iran's nearly 92 million people paints a complex picture that profoundly influences everything from infrastructure planning to environmental sustainability.
This article delves deep into the statistics, trends, and implications of Iran's population density, drawing on the latest available data. We will explore how density is calculated, its historical evolution, current figures from reputable sources like the World Bank and the UN, and what these numbers mean for the everyday lives of Iranians. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of this vital demographic indicator and its multifaceted impact on one of the Middle East's most influential nations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Population Density: A Foundational Look
- Iran's Population Growth: A 20th-Century Surge
- Current Snapshot: Iran's Population Density in Focus
- Demographic Trends Shaping Iran's Density
- Uneven Distribution: Urbanization and Regional Disparities
- The Implications of Population Density for Iran
- Projecting the Future of Iran's Population Density
- Conclusion: Navigating the Demographic Landscape
Understanding Population Density: A Foundational Look
Before diving into the specifics of Iran, it's essential to grasp what population density truly represents. At its core, population density is a simple metric: it's the midyear population divided by the land area in square kilometers. This figure provides an average measure of how many people inhabit a given unit of land. It helps us understand how crowded or sparse a country, region, or city might be. For Iran, this calculation takes into account its total area, which is the sum of land and water areas within its international boundaries and coastlines. The total area of Iran is approximately 1,648,195 km² (636,372 mi²). It's a vast country, characterized by diverse geographical features, from arid deserts and rugged mountains to fertile plains and coastal regions. This geographical diversity inherently leads to an uneven distribution of its population, making the average population density of Iran an interesting, yet sometimes misleading, figure without further context. Understanding this metric is crucial for various national and local projects. For instance, population density is typically used for infrastructure design, urban planning to allocate and distribute public services, and to assess the environmental impact of human activity based on where people are concentrated. It informs decisions on housing, transportation, healthcare, education, and resource management, directly affecting the quality of life for millions.Iran's Population Growth: A 20th-Century Surge
To appreciate Iran's current population density, it's vital to look at its recent demographic history. Iran's population experienced a dramatic increase during the latter half of the 20th century. This period saw rapid growth, leading to a significant expansion of its demographic base. By 2016, the population had reached about 80 million, a substantial leap from earlier decades. This rapid growth was influenced by various factors, including improved healthcare, reduced mortality rates, and high fertility rates characteristic of many developing nations during that era. The demographic dividend resulting from this growth brought both opportunities and challenges, putting pressure on resources and infrastructure but also providing a large, young workforce. However, recent years have witnessed a notable shift in this trend. Iran's birth rate has dropped significantly, signaling a transition in its demographic profile. While the population continues to grow, the pace has slowed. As of November 2024, Iran's population is around 91.5 million. More precisely, as of July 1, 2024, the population of Iran (Islamic Republic of) reached 91,567,738, with a slight male majority: 46,532,056 males to 45,035,681 females. The overall population growth rate for the year is estimated at 0.989%. This transition from rapid growth to a more moderate pace has profound implications for the future population density of Iran.Current Snapshot: Iran's Population Density in Focus
Now, let's zero in on the core of our discussion: the current population density of Iran. This figure provides a real-time understanding of how many people are living within each square kilometer of the country's land area.How Density is Calculated for Iran
As previously mentioned, population density is calculated by dividing the permanently settled population of Iran by the total area of the country. The total area, encompassing both land and water within its borders, is crucial for this calculation. With a total area of approximately 1,648,195 km², Iran is the 17th largest country in the world, offering vast expanses that are both habitable and uninhabitable. This large landmass plays a significant role in determining its overall population density.Key Figures and Variations
Different sources provide slightly varying figures for Iran's population density, often due to the specific year of data collection or minor differences in land area calculations. However, they consistently point to a moderate density compared to many other nations. * In 2022, according to the World Bank collection of development indicators, compiled from officially recognized sources, the population density (people per sq. Km of land area) in Iran was reported at 55.18 people per sq. Km. * The UN’s data portal estimated the population density as 56 people/km² in 2024. * Another calculation for 2024, based on a total land area of 1,628,550 km², places the density at 56 people per km² (146 people per mi²). * As of July 1, 2024, with a population of 91,567,738, the country has a population density of 56.2196 people per square kilometer. * Looking slightly ahead, Iran's population density is projected to be 53.9 people per square kilometer (139.7/mi²) as of July 2025. These figures indicate a relatively stable population density of Iran in the mid-50s (people per sq. km) range in recent years. This level suggests that while Iran has a large population, its vast land area means it is not as densely packed as some smaller, highly urbanized countries. However, this average figure masks significant internal variations, which we will explore further.Demographic Trends Shaping Iran's Density
The current and future population density of Iran are not just products of its land area and total population; they are deeply influenced by underlying demographic trends. These include birth rates, age structure, sex ratio, and urbanization patterns.The Declining Birth Rate
One of the most significant demographic shifts in Iran in recent years has been the sharp drop in its birth rate. After decades of high fertility, the total fertility rate (TFR) has fallen considerably. This decline is a critical factor influencing future population growth and, consequently, population density. A sustained low birth rate will eventually lead to a stabilization or even a decrease in the overall population, which in turn could lead to a decrease in the population density of Iran, especially if the population doesn't continue to grow. This trend is already being observed, with projections indicating that Iran's population density is expected to be decreasing for the next 50 years.Age Structure and Sex Ratio
The population pyramid of Iran provides insights into its age structure, which is vital for understanding its demographic momentum. While specific detailed data for the most current population pyramid is complex, the available information suggests a maturing population. Iran's population structure shows a slightly higher male-to-female ratio of 1.03 to 1. The median male age is approximately 34.21 years old, and the median female age is 34.61 years old. This indicates a relatively young to middle-aged population, but with an aging trend compared to the youthful bulge of previous decades. The median age is a crucial indicator. As the median age increases, it signifies a shift towards an older population, which can have implications for the dependency ratio (the ratio of dependents—young and old—to the working-age population), labor force, and social welfare systems. While not directly impacting current density figures, these trends will shape the future population size and distribution, indirectly influencing the population density of Iran in the long term.Uneven Distribution: Urbanization and Regional Disparities
While the average population density of Iran stands at around 56 people per square kilometer, this figure conceals significant disparities in how people are distributed across the country. Iran is a highly urbanized nation, and its population is far from evenly spread. Urbanization is a dominant trend. Tehran, the administrative capital and main commercial center, exemplifies this concentration. It is one of the largest cities in the Middle East and the largest city in Iran. Its metropolitan area is home to millions, creating extremely high local population densities that contrast sharply with the national average. This urban magnet effect is also seen in other major cities and provincial capitals. The "Population of Iranian provinces and counties in 2021" data would show a stark contrast between densely populated provinces, particularly in the north and west, and the vast, arid central and eastern regions, which remain sparsely inhabited. Areas like the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut deserts are virtually unpopulated, contributing significantly to the large land area that dilutes the national average population density. This uneven distribution means that while the country as a whole might not appear overly crowded, its major urban centers face challenges associated with high population concentrations, such as traffic congestion, housing shortages, and strain on public services.The Implications of Population Density for Iran
The population density of Iran, both at the national average and its highly varied regional levels, has profound implications across multiple sectors. * **Infrastructure and Urban Planning:** High population densities in cities like Tehran necessitate extensive investment in infrastructure—roads, public transport, water supply, and sanitation. Urban planning becomes critical for managing growth, preventing sprawl, and ensuring livable conditions. The challenge lies in efficiently allocating and distributing public services to meet the needs of concentrated populations. * **Resource Management:** A growing population, especially when concentrated, puts immense pressure on natural resources. Water scarcity, a significant issue in many parts of Iran, is exacerbated by high population densities. Energy consumption also rises. Understanding where people are concentrated helps in strategic resource allocation and sustainable management practices. * **Environmental Impact:** Human activity, particularly in dense urban areas, has a considerable environmental footprint. Air pollution, waste generation, and habitat destruction are common challenges in highly populated regions. Assessing the environmental impact requires precise data on where people are concentrated, guiding efforts towards environmental protection and sustainable development. * **Economic Development:** Population density can influence economic activity. Densely populated areas often become economic hubs, fostering innovation and commerce due to the concentration of labor and markets. However, over-density can also lead to unemployment and underemployment if job creation doesn't keep pace with population growth. * **Social Services:** The provision of social services like healthcare, education, and housing is directly tied to population distribution. High-density areas require more schools, hospitals, and housing units, while remote, low-density areas face challenges in providing accessible services. The intricate relationship between population density and these critical areas underscores why this demographic indicator is not just a number, but a vital tool for policymakers and planners in Iran.Projecting the Future of Iran's Population Density
Looking ahead, the future of the population density of Iran will be shaped by the interplay of several factors: continued urbanization, the declining birth rate, and potential migration patterns. As per current trends, Iran's population density is expected to be decreasing for the next 50 years. This projection is largely driven by the significant drop in the total fertility rate. If the birth rate remains low and does not rebound, the rate of population growth will continue to slow, eventually leading to a stabilization or even a decline in the total population. Given Iran's vast land area, a slower growing or declining population would naturally lead to a lower overall population density. However, internal migration towards urban centers is likely to continue. This means that while the national average density might decrease, the density in major cities could continue to increase, exacerbating urban challenges. Therefore, future planning must consider both the macro-level demographic shifts and the micro-level realities of urban concentration. Policies promoting balanced regional development and incentivizing settlement in less dense areas could become increasingly important to manage the distribution of the population more equitably. Exploring population data in Iran, including growth rate, density, key demographics, births, deaths, and more, becomes crucial for accurate future projections. The population pyramid, age structure, sex ratio, life expectancy, and dependency ratio will all play a role in shaping the country's demographic future and, consequently, its population density.Conclusion: Navigating the Demographic Landscape
The population density of Iran is a dynamic and multifaceted indicator, reflecting the country's past growth, current demographic realities, and future challenges. With a population of over 91.5 million and an average density hovering around 56 people per square kilometer, Iran presents a unique case study of a large nation grappling with both overall population growth and significant internal redistribution. The dramatic population surge of the late 20th century has given way to a period of declining birth rates, which is projected to lead to a decreasing national population density in the coming decades. However, this macro trend is offset by the intense urbanization, with major cities like Tehran experiencing high concentrations of people. This uneven distribution poses distinct challenges for urban planning, infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental sustainability. Understanding these complexities is vital for policymakers, researchers, and anyone interested in Iran's development trajectory. The data from the World Bank, the UN, and national statistics provides a clear picture of Iran's demographic landscape, highlighting the need for strategic planning to ensure a sustainable and prosperous future for all its citizens. What are your thoughts on Iran's demographic shifts? Do you think the declining birth rate will significantly alter the country's urban challenges? Share your insights in the comments below, and don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more in-depth analyses of global demographic trends!
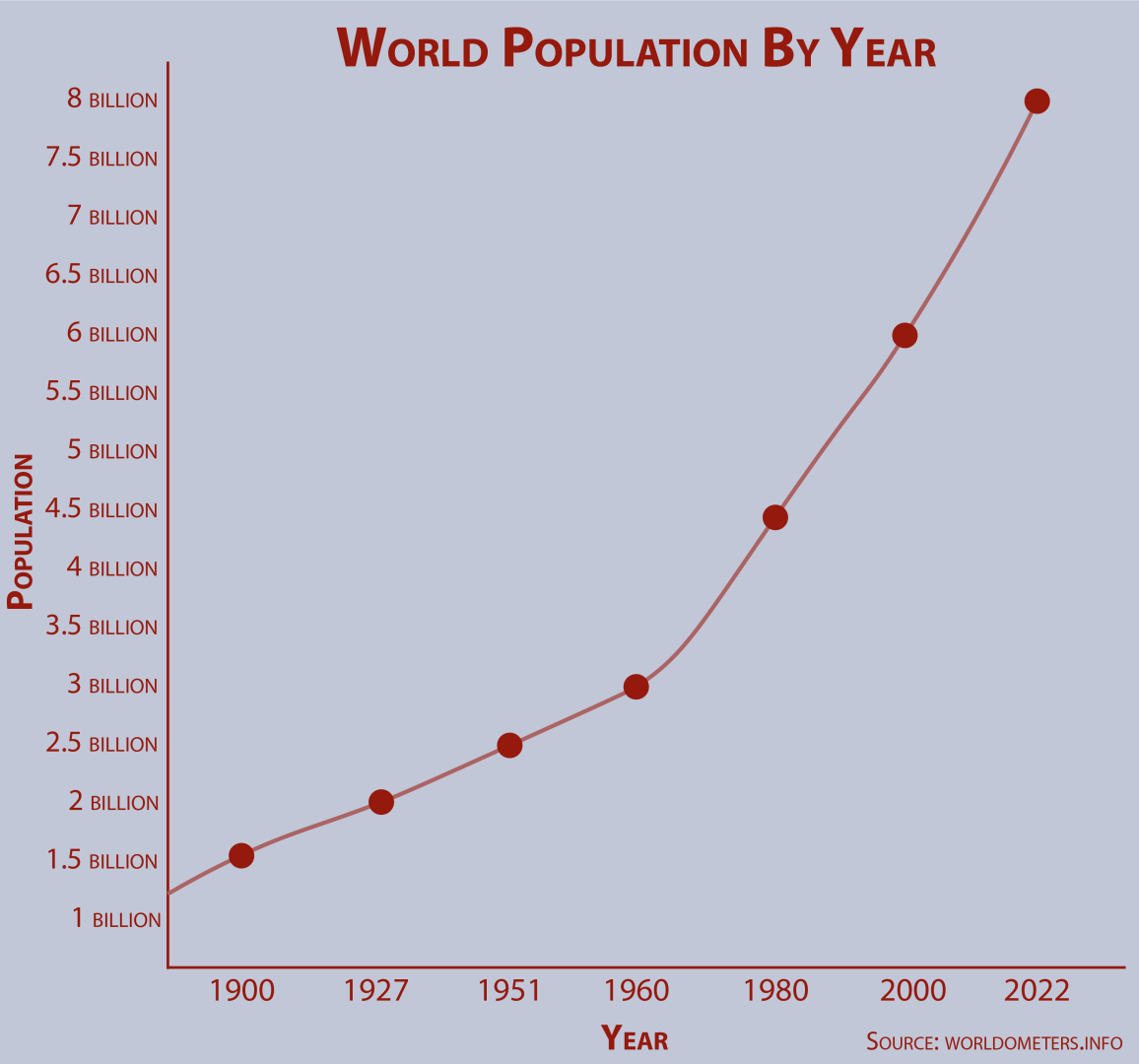
World population could peak at 8.5 billion people by the 2050s, study
Population Year 2022 - Worldmapper
Global population reaches eight billion – The Reflector