Iran's Population: Unpacking The Latest Demographic Shifts
Table of Contents
- A Glimpse into Iran's Demographic Tapestry
- Iran's Population Growth: A Historical Perspective
- Current and Projected Population: What the Numbers Say
- Key Demographic Indicators Shaping Iran's Future
- Population Distribution: Provinces and Urbanization
- Migration and its Impact on Iran's Demographics
- Understanding the Population Pyramid and Sex Ratio
- Life Expectancy and Public Health in Iran
- Conclusion: Charting Iran's Demographic Future
A Glimpse into Iran's Demographic Tapestry
Iran's population, a mosaic of diverse ethnicities and cultures, is constantly evolving. To truly grasp the significance of the latest statistics, it's essential to consider the broader demographic tapestry that encompasses current, historical, and projected population figures, alongside crucial indicators like growth rate, immigration patterns, median age, total fertility rate (TFR), population density, and urbanization trends. These elements collectively paint a comprehensive picture of a nation in demographic transition. The availability of detailed data, including the population of Iranian provinces and counties, allows for a granular understanding of regional variations within this overarching narrative. This article will draw upon these specific data points to provide an in-depth analysis. The dynamic nature of Iran's population means that figures are constantly updated. For instance, while estimates vary slightly depending on the source and methodology, the general consensus points to a significant increase in recent decades, followed by a more complex period of fluctuating growth. Understanding these shifts is not merely an academic exercise; it has profound implications for national planning, resource allocation, and social development. The focus here is on presenting the most relevant and up-to-date statistics to provide a clear and actionable insight into Iran's demographic reality.Iran's Population Growth: A Historical Perspective
The story of Iran's population growth is one of dramatic shifts, particularly over the last century. From relatively stable numbers for centuries, the nation experienced an unprecedented demographic boom that reshaped its society. Tracing this historical trajectory provides essential context for understanding the current state of the population of Iran.The Early Centuries: Slow and Steady
For a significant period, from 1880 until 1920, the population of Iran remained remarkably stable, hovering at 10 million or below. This era was characterized by various factors that kept population growth in check, including limited healthcare, lower life expectancy, and the impact of regional conflicts and socio-economic conditions. The pace of life was slower, and demographic changes were gradual, reflecting patterns common in many pre-industrial societies. This long period of stability provides a baseline against which to measure the dramatic changes that followed.The 20th Century Boom: From 10 Million to 80 Million
The mid-20th century marked a pivotal turning point for Iran's population. From 1920 onwards, the population began to increase steadily, reaching 20 million by 1955. This acceleration was largely driven by improvements in public health, sanitation, and a decline in mortality rates. The most drastic increase, however, occurred in the latter half of the 20th century. According to statistics, the population reached 50 million in 1985, a remarkable surge in just three decades. This rapid expansion continued, with Iran's population increasing dramatically to reach about 80 million by 2016. This period of rapid growth presented both opportunities and challenges for the nation, necessitating significant investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare to accommodate the burgeoning numbers.Current and Projected Population: What the Numbers Say
Pinpointing the exact current population of Iran can be challenging due to the dynamic nature of demographic data, but projections based on reliable sources provide a clear picture. The latest estimates from the United Nations offer the most comprehensive and widely accepted figures, allowing us to understand both the present and the near future of the population of Iran.Navigating 2024 and 2025 Projections
According to the United Nations' 2024 revision of World Population Prospects, which presents population estimates from 1950 to the present, the total population in Iran is projected at 91,567,738, or 91.57 million people, for the year 2024. This figure aligns closely with other recent estimates, such as the statement that as of November 2024, Iran's population is around 91.5 million. Looking slightly ahead, the population of Iran is projected at 92,417,681, or 92.42 million, as of July 1, 2025, based on interpolation of the latest United Nations data. Another specific projection states the current population of Iran is 92,426,406 as of July 06, 2025, also based on interpolation of the latest United Nations data. These projections indicate a continued, albeit slower, growth trajectory. It is worth noting that some other figures are also cited, such as "Total current population for Iran in 2025 is 90,410,659, a 0.67% increase from 2024," and "Total population for Iran in 2024 was 89,809,781, a 0.88% decline from 2023." While these figures suggest a different trend (a decline from 2023 to 2024 in one instance), the United Nations data, which provides consistent projections for both 2024 and 2025, offers a more harmonized view of the current and projected growth. The latest data also indicates that the population crossed the 86 million mark in the final days of the Iranian calendar year 1403 (ending March 2025), further confirming the upward trend, even if the pace is moderating. These numbers are vital for policymakers to plan for future resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services.Key Demographic Indicators Shaping Iran's Future
Beyond the raw numbers of the population of Iran, several key demographic indicators provide deeper insights into the country's societal structure and future trajectory. These include the total fertility rate, median age, age structure, and dependency ratio, all of which are critical for understanding the evolving demographic landscape.Total Fertility Rate (TFR) and Birth Rate Decline
One of the most significant shifts in Iran's demographic profile in recent years has been the dramatic drop in its birth rate. This is directly reflected in the Total Fertility Rate (TFR), which measures the average number of children a woman is expected to have over her lifetime. A TFR of approximately 2.1 is generally considered the replacement level, meaning the population will remain stable without migration. Iran's TFR has fallen significantly, indicating a shift towards smaller family sizes. This decline is influenced by a multitude of factors, including increased access to education for women, urbanization, changes in socio-economic conditions, and family planning initiatives. The implications of a falling birth rate are far-reaching, affecting the future workforce, the dependency ratio, and the overall age structure of the population.Median Age, Age Structure, and Dependency Ratio
The median age of a population is a crucial indicator, dividing the population into two halves: one younger and one older. As birth rates decline and life expectancy generally increases, the median age tends to rise, indicating an aging population. Iran is experiencing this demographic shift, moving from a predominantly young population to one with a growing proportion of middle-aged and older individuals. This change in age structure is visually represented by the population pyramid, which illustrates the distribution of various age groups by sex. Accompanying the changing age structure is the dependency ratio, which compares the number of dependents (children and elderly) to the working-age population. A high dependency ratio can place a significant burden on the working population to support the younger and older segments of society. As Iran's population ages, the old-age dependency ratio is expected to increase, posing challenges for social security systems, healthcare, and pension funds. Understanding these interconnected indicators is vital for long-term national planning and policy formulation.Population Distribution: Provinces and Urbanization
The distribution of the population of Iran across its vast geography is uneven, with significant concentrations in urban centers and certain provinces. Analyzing this distribution provides insights into regional development, internal migration patterns, and the challenges associated with rapid urbanization. Data regarding the population of Iranian provinces and counties in 2021 highlights these disparities. Major cities and their surrounding provinces often serve as economic hubs, attracting internal migrants seeking better opportunities, which further exacerbates population density in these areas. This trend of urbanization has been a defining feature of Iran's demographic landscape for decades. As more people move from rural areas to cities, it puts pressure on urban infrastructure, housing, and public services, while also leading to depopulation in some rural regions. The balance between urban and rural populations, and the specific densities within different provinces, are crucial considerations for regional planning and equitable development.Migration and its Impact on Iran's Demographics
Beyond births and deaths, migration plays a significant role in shaping the population of Iran. This includes both internal migration (movement within the country) and international migration (movement across borders). While precise net migration figures can be complex to ascertain, their impact on demographic trends is undeniable. International migration, encompassing both emigration (people leaving Iran) and immigration (people entering Iran), influences the overall population size and its composition. Iran has historically been a host country for refugees, particularly from neighboring Afghanistan, which has contributed to its population figures. Conversely, economic and social factors can lead to emigration, particularly among skilled professionals and youth. These movements affect not only the total population but also the age structure, sex ratio, and economic productivity. Understanding the push and pull factors of migration is essential for a holistic view of Iran's demographic evolution and for formulating policies that address the challenges and opportunities presented by these population movements.Understanding the Population Pyramid and Sex Ratio
The population pyramid is a graphical representation that illustrates the distribution of various age groups in a population, typically separated by sex (males to females). For the population of Iran, analyzing its pyramid reveals crucial insights into its past demographic events and future potential. Historically, Iran's population pyramid would have shown a broad base, indicative of high birth rates and a young population. As birth rates have declined, the base of the pyramid has narrowed, reflecting fewer younger individuals. The bulge in the middle sections of the pyramid represents the large cohorts born during the high-growth periods of the late 20th century. As these cohorts age, the pyramid will continue to transform, becoming more rectangular or even inverted at the top, signifying an aging population. The sex ratio (males to females) at different age groups within the pyramid can also reveal important societal trends, such as gender imbalances at birth, differences in life expectancy between sexes, or the impact of migration patterns. These visual representations are powerful tools for demographers and policymakers to quickly grasp complex demographic structures.Life Expectancy and Public Health in Iran
Life expectancy at birth is a fundamental indicator of a population's overall health and well-being. It reflects the average number of years a newborn is expected to live if current mortality rates continue. For the population of Iran, improvements in life expectancy over the decades underscore advancements in healthcare, sanitation, and living standards. As life expectancy generally increases, it contributes to the aging of the population, impacting social welfare systems and healthcare demands. The rise in life expectancy in Iran is a testament to progress in public health initiatives, disease control, and access to medical services. However, challenges remain, including the prevalence of non-communicable diseases and the need for robust healthcare infrastructure to support an aging populace. Monitoring life expectancy alongside other demographic indicators like births, deaths, and migration is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of public health policies and for planning future healthcare provisions.Conclusion: Charting Iran's Demographic Future
The population of Iran is in a fascinating state of transition, marked by a rich history of rapid growth and more recent shifts towards moderated fertility rates and an aging demographic profile. From the stable millions of the early 20th century to the 91.5 million recorded in November 2024, and projected to reach 92.42 million by July 2025, Iran's demographic journey is a testament to its evolving socio-economic landscape. Key indicators such as the declining Total Fertility Rate, the rising median age, and the increasing urbanization all point towards a future with distinct challenges and opportunities. Understanding these complex demographic trends is not just an academic exercise; it is fundamental for Iran's sustainable development, resource management, and social planning. The data, based on authoritative sources like the United Nations, provides a robust foundation for informed decision-making. As Iran continues to navigate these demographic shifts, the insights gained from analyzing its population statistics will be invaluable for shaping policies that ensure the well-being and prosperity of its people. We hope this comprehensive overview has provided valuable insights into the latest statistics concerning the population of Iran. What are your thoughts on these demographic trends? Do you have any questions or additional perspectives to share? Feel free to leave a comment below and join the conversation. For more in-depth analyses of global demographic patterns, explore other articles on our site.
World population could peak at 8.5 billion people by the 2050s, study
Population Year 2022 - Worldmapper
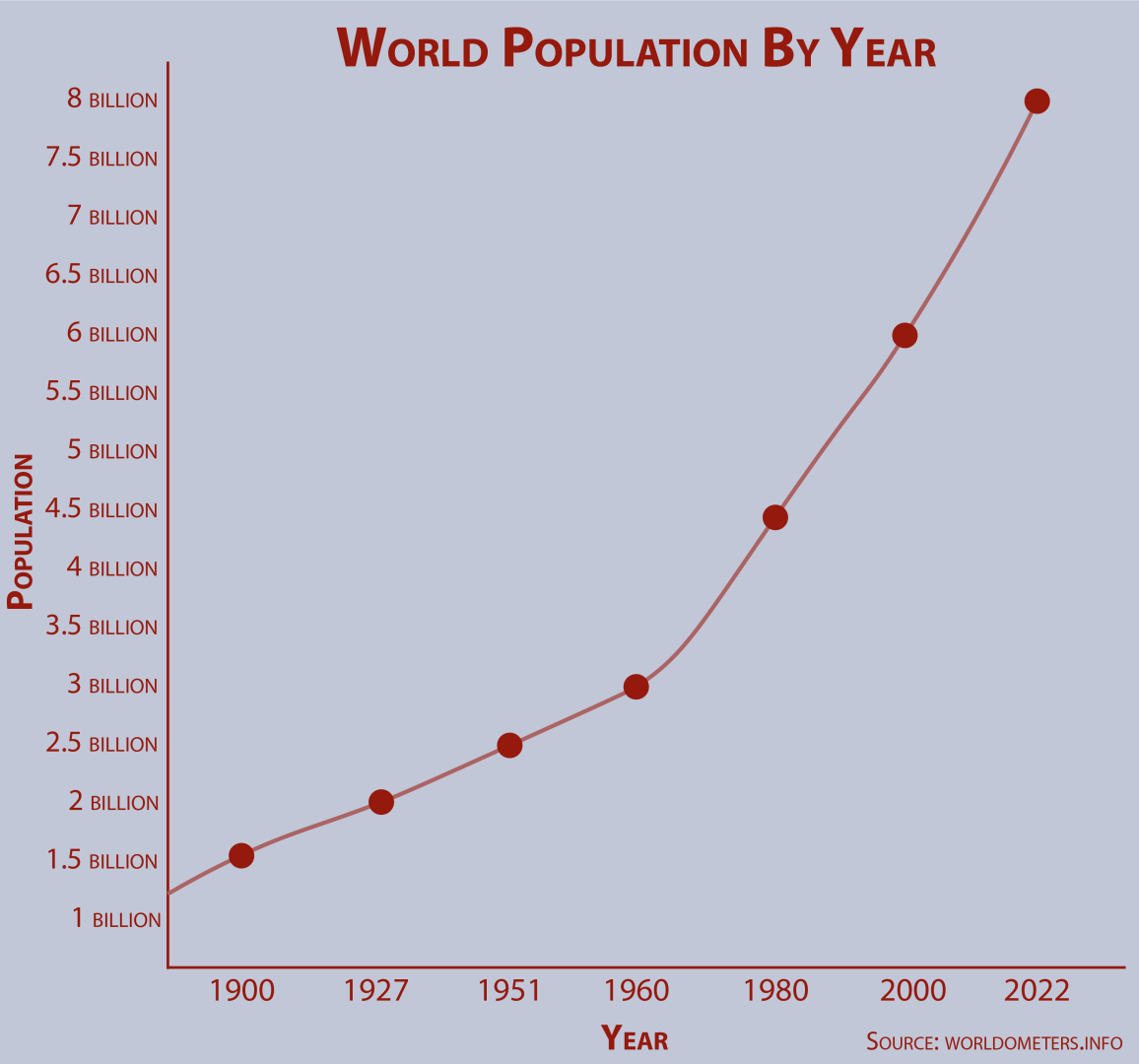
Global population reaches eight billion – The Reflector