Iran Vs. Israel: Unpacking Their Current Military Strength
In the tumultuous landscape of the Middle East, two nations stand out for their military might and strategic importance: Iran and Israel. The ongoing tensions, particularly highlighted by recent escalations, have brought renewed focus on the military capacities of each country. Understanding the nuances of their respective armed forces is crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend the intricate geopolitical dynamics of the region. This article provides a detailed analysis of the current military strength comparison between Iran and Israel, exploring their capabilities, technology, and strategic advantages.
Both countries boast formidable armies and advanced air forces, and in the case of Iran, a controversial nuclear program. As regional powers, they play significant roles in shaping the future of the Middle East. With Israel having vowed to retaliate for Iran's recent missile attack, prompting fears of an escalating conflict, a comprehensive examination of their military postures becomes not just academic, but critically important for assessing potential outcomes.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Rivalry
- The Human Element: Manpower and Reserves
- Air Power: The Decisive Edge?
- Ground Forces: Tanks, Artillery, and Mechanized Might
- Naval Capabilities: Strategic Presence
- Technological Superiority and Defense Budgets
- Strategic Capabilities and Nuclear Ambitions
- Regional Implications and Future Outlook
- Conclusion: Balancing the Scales
Introduction to the Rivalry
The geopolitical chessboard of the Middle East is perpetually in motion, with Iran and Israel often positioned as primary antagonists. Their rivalry is multifaceted, encompassing ideological differences, proxy conflicts, and a strategic competition for regional influence. This dynamic tension frequently manifests in military posturing, making a current military strength comparison Iran Israel a topic of immense interest and strategic importance. As 24/7 Wall St notes, understanding their respective capabilities is key to deciphering potential conflict scenarios.
- Mm2 Values Trading
- Mr Bean Death News
- Did Charlie Sheen Have A Daughter That Died
- Ben Napiers Health Update
- Uncle June Pizza
In 2025, tensions in the Middle East remain high, underscoring the ongoing relevance of this military assessment. The global rank value for both nations, derived from defense aggregate GlobalFirepower.com, along with their regional rankings, offers a theoretical military firepower comparison by conventional means. This provides a foundational understanding before diving into the specifics of their forces. The force emphasis, a broad reflection on the focus placed on each military branch, also plays a crucial role in defining their strategic doctrines.
The Human Element: Manpower and Reserves
When assessing the current military strength comparison Iran Israel, the sheer number of personnel is often the first metric considered. While quantity doesn't always equate to quality, a larger force can sustain longer conflicts and cover more ground. This is particularly evident in the contrasting approaches of Iran and Israel to military service and reserve mobilization.
Iran's Numerical Superiority
Iran boasts a significantly larger military force in terms of active personnel and reserves. Military service is compulsory for Iranian men over the age of 18, contributing to a vast pool of trained individuals. Iran has 610,000 active military personnel, a figure that includes 350,000 in the army, 190,000 in the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), 18,000 in the navy, 37,000 in the air force, and 15,000 in air defense. Beyond its active forces, Iran’s reserve forces number an additional 350,000, bringing its total potential manpower to nearly a million. This numerically greater manpower, especially in ground forces and navy, gives Iran a distinct advantage in terms of sheer scale, as highlighted in various analyses, including those from 24/7 Wall St.
- Thejup Exchcom Jupiter Exchange
- Nat Wolfe
- Pizzas By Sadik
- Gooya News Persian News
- What Nationality Is Katie Miller
Israel's Robust Reserve System
In contrast, Israel's active military personnel numbers are considerably smaller, but its strength lies in its robust reserve system. Israel has 170,000 active military personnel, along with an impressive 465,000 reserves and 35,000 paramilitary forces. This robust reserve system means that while Israel's standing army is smaller, it can rapidly expand its forces with highly trained individuals in times of crisis. The quality of training and the integration of reserves into operational units are key factors that offset Iran's numerical advantage. This allows Israel to maintain a high level of readiness and responsiveness, despite its smaller active force size. The ability to quickly mobilize and deploy a large number of experienced personnel is a critical component of Israel's defense strategy.
Air Power: The Decisive Edge?
In modern warfare, air power is often considered the decisive element, capable of shaping the battlefield, projecting power, and neutralizing threats from a distance. In the current military strength comparison Iran Israel, this is where the scales significantly tip in Israel's favor. While Iran has numerically greater manpower, Israel is superior to its adversary in terms of air power and technology—elements often considered decisive in contemporary conflicts.
Israel possesses a highly advanced air force, equipped with cutting-edge fighter jets, attack helicopters, and sophisticated air defense systems, many of which are supplied by the United States. Its fleet includes F-35 stealth fighters, F-16s, and F-15s, which are regularly upgraded and maintained at peak operational efficiency. The Israeli Air Force (IAF) is renowned for its pilot training, operational experience, and technological superiority, allowing it to maintain air superiority over its adversaries. This technological edge is a critical component of Israel's military doctrine, enabling precision strikes and effective defense against aerial threats.
Conversely, Iran's air force, while substantial in personnel (37,000 in the air force and 15,000 in air defense), relies on an aging fleet of aircraft, many of which are remnants from before the 1979 revolution or older Russian and Chinese models. The IISS (International Institute for Strategic Studies) reports that Iran has around 334 combat aircraft, despite more than 25,000 personnel dedicated to its air force. Decades of sanctions have severely hampered Iran's ability to acquire modern aircraft and spare parts, forcing it to rely on domestic production and maintenance of older platforms. While Iran has made efforts to develop its own drones and missile capabilities to compensate for its air force deficiencies, its conventional air power remains significantly outmatched by Israel's.
Ground Forces: Tanks, Artillery, and Mechanized Might
The ground forces represent the backbone of any military, responsible for holding territory, engaging in direct combat, and conducting prolonged operations. In a current military strength comparison Iran Israel, Iran holds a numerical advantage in this domain, but Israel's qualitative edge in technology and training is a significant counterpoint.
Iran's army, with 350,000 active personnel, operates a large inventory of tanks, armored personnel carriers, artillery pieces, and rocket launchers. Much of this equipment, similar to its air force, is older and domestically produced or reverse-engineered. While Iran has invested in developing its own armored vehicles and missile systems, the overall technological sophistication and combat readiness of its ground forces are often questioned compared to Western standards. The IRGC, a parallel military force, also maintains its own ground units, which are often better equipped and trained, playing a crucial role in Iran's regional influence operations.
Israel's ground forces, though smaller in active numbers, are highly mechanized, well-trained, and equipped with some of the most advanced military hardware in the world. The Merkava main battle tank, designed and manufactured domestically, is considered one of the best-protected tanks globally. Israel also possesses advanced armored personnel carriers, self-propelled artillery, and precision-guided munitions. The emphasis on technology, combined with extensive combat experience from numerous conflicts, gives Israeli ground units a significant qualitative advantage. Their ability to integrate intelligence, air support, and ground maneuvers seamlessly makes them a highly effective fighting force.
Naval Capabilities: Strategic Presence
Naval power, while perhaps less central to a direct land conflict between Iran and Israel, plays a crucial role in projecting power, securing maritime routes, and conducting asymmetric warfare. In the current military strength comparison Iran Israel, Iran possesses a numerically larger navy, particularly in terms of smaller, fast-attack craft, while Israel's navy focuses on high-tech, multi-mission vessels.
Iran's navy, including the regular navy and the IRGC Navy, operates a diverse fleet designed primarily for defensive operations in the Persian Gulf and asymmetric warfare. It comprises numerous fast-attack craft, patrol boats, submarines (including domestically produced midget submarines), and a limited number of larger frigates and corvettes. The IRGC Navy, in particular, emphasizes swarming tactics with small, heavily armed boats, along with anti-ship missiles and naval mines, posing a significant threat to shipping in the Strait of Hormuz. Iran's naval strategy is geared towards denying access and disrupting maritime traffic rather than conventional blue-water operations.
Israel's navy is smaller but highly advanced, focusing on quality over quantity. Its primary missions include coastal defense, protecting offshore gas platforms, and conducting special operations. The Israeli Navy operates highly capable corvettes, missile boats, and advanced submarines (Dolphin-class), which are believed to have second-strike nuclear capabilities. These submarines are equipped with advanced sensors and long-range missiles, providing a strategic deterrent. Israel's naval vessels are equipped with sophisticated electronic warfare systems and air defense capabilities, designed to operate effectively in contested waters and protect vital national interests.
Technological Superiority and Defense Budgets
Beyond raw numbers, the technological sophistication of military equipment and the financial resources allocated to defense are critical determinants of military strength. A detailed analysis of Israel's military strength vs. Iran's reveals stark differences in these areas.
Innovation vs. Quantity
Israel consistently invests heavily in defense research and development, fostering a vibrant defense industry known for its innovation. This focus on technology has led to advancements in areas such as missile defense (e.g., Iron Dome, David's Sling, Arrow system), cyber warfare, intelligence gathering, and precision-guided munitions. Israel's military doctrine relies on leveraging technological superiority to overcome numerical disadvantages. Its close strategic alliance with the United States also provides access to advanced military hardware and intelligence sharing, further enhancing its technological edge. This emphasis on cutting-edge technology is a cornerstone of Israel's approach to maintaining its qualitative military advantage.
Iran, on the other hand, faces significant challenges in acquiring advanced military technology due to international sanctions. This has forced it to develop a robust domestic defense industry, focusing on reverse engineering, indigenous production of missiles, drones, and armored vehicles. While Iran has made impressive strides in missile and drone technology, producing a wide array of ballistic and cruise missiles, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), its overall technological base for conventional forces lags behind Israel's. The quality control, integration of systems, and precision of Iranian-made equipment often fall short of Western standards, impacting their effectiveness in high-intensity conventional conflicts. However, the sheer quantity and increasing sophistication of its missile and drone arsenal present a significant threat, as demonstrated by recent events.
Financial Firepower
Defense budgets reflect a nation's commitment to its military and its capacity to procure, maintain, and develop advanced systems. While exact figures can vary and are often opaque, general trends provide insight into the financial firepower of each nation.
Israel consistently allocates a substantial portion of its GDP to defense, ranking among the highest globally in per capita military spending. This robust defense budget, coupled with significant military aid from the United States, allows Israel to maintain a technologically advanced military, invest in cutting-edge research, and conduct regular training exercises. The ability to afford and integrate the latest military innovations is a key factor in Israel's qualitative advantage.
Iran's defense spending, while substantial in absolute terms for a regional power, faces constraints due to its economic challenges and international sanctions. Much of its budget is allocated to maintaining its large standing army, supporting its missile and drone programs, and funding proxy groups in the region. While Iran has demonstrated an ability to produce military equipment domestically, the scale and sophistication of its procurement are limited compared to Israel's access to global markets and advanced Western technologies. This disparity in financial firepower directly impacts the modernization and technological advancement of their respective militaries.
Strategic Capabilities and Nuclear Ambitions
Beyond conventional forces, strategic capabilities, including long-range missile programs, cyber warfare, and the controversial nuclear dimension, significantly influence the power balance in the current military strength comparison Iran Israel.
The Nuclear Question
Perhaps the most contentious aspect of Iran's strategic capabilities is its nuclear program. While Iran consistently maintains its nuclear program is for peaceful purposes, many international observers, including Israel and Western nations, suspect it aims to develop nuclear weapons. Iran has made significant advancements in uranium enrichment, raising concerns about its "breakout time" to produce fissile material for a bomb. The potential for Iran to acquire nuclear weapons is a primary driver of Israel's security concerns and its willingness to take preemptive action.
Israel, while maintaining a policy of deliberate ambiguity, is widely believed to possess a significant arsenal of nuclear weapons. This undeclared nuclear capability serves as a powerful deterrent, a "Samson Option" in its strategic calculus, ensuring its survival against overwhelming conventional threats. The existence of an Israeli nuclear deterrent adds a layer of complexity and extreme caution to any direct military confrontation between the two nations.
Both nations also possess significant missile arsenals. Iran has one of the largest and most diverse ballistic missile programs in the Middle East, capable of striking targets across the region, including Israel. These missiles, along with its growing drone capabilities, are designed to compensate for its conventional air force deficiencies and serve as a primary means of projecting power and deterring adversaries. Israel, in turn, possesses its own advanced missile capabilities, including Jericho ballistic missiles, and robust multi-layered missile defense systems designed to intercept incoming threats from short to long ranges.
In the realm of cyber warfare, both countries are recognized as significant actors. They possess sophisticated cyber capabilities for espionage, sabotage, and defensive operations, adding another dimension to their ongoing strategic competition. Cyberattacks could precede or accompany conventional military action, aiming to disrupt critical infrastructure or military command and control systems.
Regional Implications and Future Outlook
The current military strength comparison Iran Israel is not merely an academic exercise; it has profound regional and global implications. The rivalry between these two powers fuels proxy conflicts across the Middle East, from Syria and Lebanon to Yemen and Iraq. Iran supports various non-state actors, such as Hezbollah in Lebanon and Houthi rebels in Yemen, providing them with training, funding, and advanced weaponry, including missiles and drones. These proxies serve as an extension of Iran's military reach, allowing it to exert influence and threaten Israeli interests without direct conventional engagement.
Israel, in response, conducts regular military operations to counter Iranian entrenchment in neighboring countries and to degrade the capabilities of its proxies. This "war between wars" involves airstrikes, special operations, and intelligence gathering aimed at disrupting Iran's supply lines and preventing the transfer of advanced weaponry to groups like Hezbollah. The potential for these proxy conflicts to escalate into a direct confrontation between Iran and Israel remains a constant concern, especially following recent direct missile exchanges.
The future outlook for this military dynamic is complex and uncertain. Iran will likely continue to invest in its asymmetric capabilities—missiles, drones, and naval forces—to offset Israel's technological superiority. It will also continue its efforts to develop its nuclear program, which remains a core strategic objective. Israel, for its part, will maintain its focus on qualitative military edge, advanced technology, and intelligence superiority, while striving to contain Iran's regional influence and prevent its nuclear ambitions from materializing. The ongoing competition for technological supremacy, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence and advanced weaponry, will further shape the balance of power.
Conclusion: Balancing the Scales
To compare Israel and Iran's military capabilities, using data from the Global Firepower official website and other reputable sources, reveals a nuanced picture. Iran has numerically greater manpower, ground forces, and navy than Israel. This numerical superiority provides Iran with a significant advantage in terms of sheer scale and endurance in a protracted conflict. However, Israel is superior to its adversary in terms of air power and technology—elements that are increasingly seen as the decisive factors in modern warfare.
The detailed analysis of troops, equipment, defense budgets, and strategic capabilities underscores that while Iran possesses a formidable conventional force with vast manpower and a growing indigenous arms industry, Israel compensates with superior technology, highly trained personnel, a robust reserve system, and a qualitative edge in air power. The controversial nuclear programs of both nations add an existential dimension to their rivalry, making any direct military confrontation fraught with extreme risk. The primary selection is displayed in blue while the secondary selection is displayed in red, highlighting the key strengths of each nation in various comparisons.
Ultimately, the current military strength comparison Iran Israel is not a simple matter of who has more tanks or planes. It is a complex interplay of quantity versus quality, conventional might versus asymmetric capabilities, and strategic deterrence versus regional influence. As tensions continue to simmer in the Middle East, understanding these dynamics is paramount. We encourage you to delve deeper into the specifics of military power and consider how these forces shape the geopolitical landscape. What are your thoughts on the balance of power? Share your insights in the comments below, or go back to compare two other military powers to broaden your understanding of global defense dynamics.
- Meryl Streep Daughter Actress
- Bianca Grammys Outfit
- Hayley Williams Paramore Lead Singer
- Omari Grandberry
- Noah Grey Cabey

Science is easy with me: CURRENT ELECTRICITY |class12|physicsnotes|part1

Define Current in Physics - KailabilDaniel
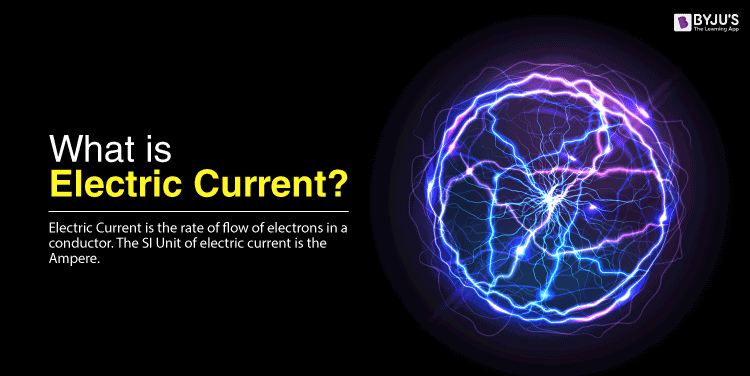
What Is Electricity: Class 10 Definition Explained