Unveiling Iran's Continent: A Deep Dive Into Its Asian Identity
Have you ever wondered about the precise geographical location of Iran? Often discussed in the context of the Middle East, its continental affiliation can sometimes be a point of curiosity for many. This article aims to definitively answer the question: what is the continent of Iran, and delve into the rich tapestry of its geography, history, and cultural significance within that continental framework.
Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a nation steeped in ancient history and vibrant culture. Its strategic location has made it a crossroads of civilizations for millennia, influencing and being influenced by various empires and cultures. Understanding its continental placement is key to appreciating its geopolitical importance and its unique identity.
Table of Contents
- Confirming Iran's Continental Identity
- Geographical Crossroads: Iran's Strategic Location
- The Vastness and Diversity of Iran's Landscape
- Historical Significance: Persia's Enduring Legacy
- Iran's Borders and Neighbors
- Cultural Identity and Regional Context
- Beyond the Borders: Iran's Global Positioning
- Why Understanding Iran's Continent Matters
Confirming Iran's Continental Identity
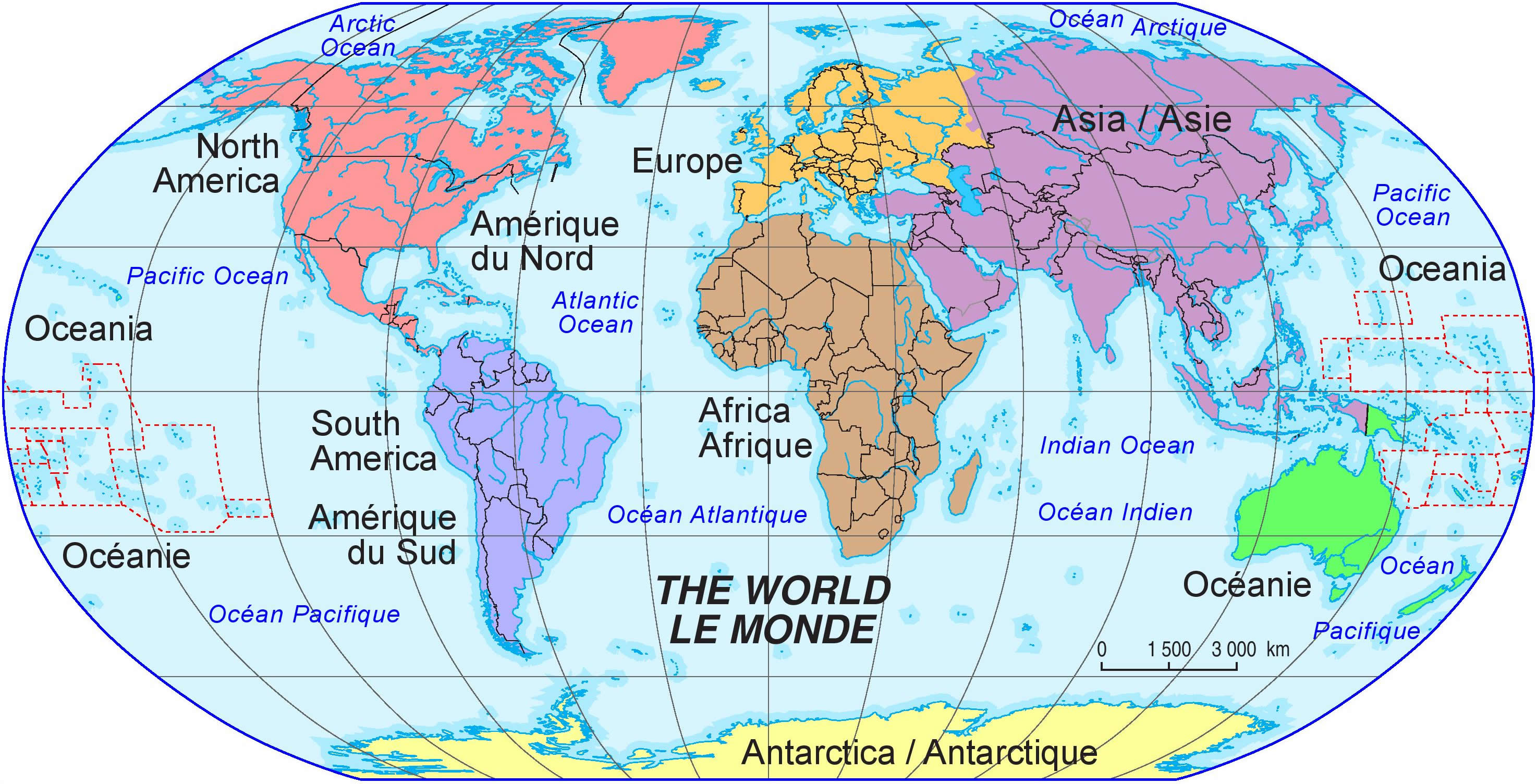
Let's cut straight to the chase: what is the continent of Iran? Iran is unequivocally located in the continent of Asia. While it is frequently referred to as being in the "Middle East," it's crucial to understand that the Middle East is a geopolitical and cultural region, not a continent itself. The Middle East is a sub-region primarily situated in Western Asia, with parts extending into North Africa and Europe. Therefore, when we speak of Iran's continental home, Asia is the correct and definitive answer.
Specifically, Iran is a country in Western Asia. This geographical classification is vital for understanding its historical trajectory, its interactions with neighboring states, and its place in global affairs. Its position as a major player in Western Asia underscores its importance both regionally and on the broader Asian stage. The country's GPS coordinates, with a latitudinal coordinate of 32.4279° N, confirm its location above the equator in the northern hemisphere, firmly placing it within the Asian landmass.
Geographical Crossroads: Iran's Strategic Location
Iran's location is more than just a dot on a map; it's a critical nexus that has shaped its destiny. As the second-largest country in the Middle East by land area, occupying an area of 1,648,195 sq. km, its vastness is impressive. Its position in Western Asia means it serves as a bridge between various sub-regions: Central Asia to the north, the Indian subcontinent to the east, the Arabian Peninsula to the south, and Anatolia and the Levant to the west. This unique geographical positioning has historically made Iran a significant player in regional power dynamics and a factor in superpower rivalries.
The "Data Kalimat" explicitly states: "Iran is located in the middle east region at latitude 32.427908 and longitude 53.688046 and is part of the Asian continent." This reiterates the dual classification – a country within the Middle East region, but fundamentally part of the Asian continent. This dual identity is crucial for comprehending its complex geopolitical landscape and its diverse cultural influences.
The Vastness and Diversity of Iran's Landscape
Beyond its continental classification, Iran's physical geography is incredibly diverse, contributing to its unique character. It is primarily a mountainous, arid, and ethnically diverse country of southwestern Asia. The landscape is dominated by rugged plateaus and mountains, with most of the land being above 1,500 feet (460 m). The high interior plateau, known as the Plateau of Iran, forms the central part of the country and is surrounded by formidable mountain ranges, including the Alborz and Zagros mountains.
Despite its arid reputation, Iran boasts a surprisingly varied nature and climate, containing abundant plants and animals. Its vegetation diversity is more than twice the size of the European continent and nearly equals the Indian subcontinent. This ecological richness is a testament to its varied topography, which includes not only deserts and mountains but also coastlines along the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south. This geographical variety has profoundly influenced its regional economies, settlement patterns, and cultural development over millennia.
Historical Significance: Persia's Enduring Legacy
The question of what is the continent of Iran becomes even more profound when we consider its historical depth. Iran, historically known as Persia, is the heart of the Persian Empire of antiquity. This ancient base of civilization and culture has long played an important role in the region as an imperial power. Since the beginnings of historical records associated with Cyrus the Great in the 6th century B.C.E., Iran (Persia) has been a formidable force.
The country has been a crossroads for conquerors and cultures. Alexander the Great brought Hellenistic culture to Persia in the 4th century B.C.E., opening the gate to a long procession of foreign dynasties and cultural exchanges. Modern Iranian culture owes itself in part to a renaissance in the 8th century, which saw a flourishing of arts, sciences, and literature that significantly contributed to the Islamic Golden Age. This rich historical narrative is intrinsically linked to its position within Asia, as it interacted with civilizations across the continent, from the Mediterranean to China.
Iran's Borders and Neighbors
A detailed look at Iran's borders further solidifies its position within the Asian continent and highlights its role as a central hub in Western Asia. Iran shares extensive land and sea borders with numerous countries, each relationship shaped by geography, history, and politics.
To the North: Caspian Sea and Central Asian Neighbors
To the north, Iran is bordered by the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. This strategic sea provides access to Central Asian states and Russia. Along its northern land borders, Iran shares boundaries with Turkmenistan to the northeast, and Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest. These borders connect Iran to the Caucasus and Central Asian regions, facilitating cultural and economic ties that have existed for centuries.
To the West: Iraq and Turkey
To the west, Iran borders Iraq and Turkey. The border with Iraq is particularly significant, given their shared history, including the Iran-Iraq War, and their cultural and religious connections. The border with Turkey links Iran to Anatolia and, by extension, to Europe, though Iran itself remains firmly in Asia. These western borders are crucial for trade routes and geopolitical considerations in the broader Middle East.
To the East: Afghanistan and Pakistan
Moving eastward, Iran shares borders with Afghanistan and Pakistan. These eastern borders connect Iran to the Indian subcontinent and the broader South Asian region. The relationships along these borders are complex, influenced by shared cultural heritage, migration patterns, and regional security concerns. The proximity to these nations further emphasizes Iran's deep roots and extensive connections within the Asian landmass.
To the South: The Gulfs
To the south, Iran is bounded by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. These vital waterways provide Iran with direct access to international shipping lanes and are central to its oil industry, a cornerstone of its economy. The Persian Gulf, in particular, is a region of immense geopolitical importance, shared with several Arab states. This southern maritime boundary is crucial for global energy markets and Iran's strategic positioning.
Cultural Identity and Regional Context
While we've firmly established what is the continent of Iran (Asia), it's also important to understand its cultural identity within the broader regional context. Iran is a country in the Middle East, a region known for its rich history, diverse cultures, and significant religious heritage. This regional identity is deeply intertwined with its continental placement. Its culture is a unique blend of ancient Persian traditions, Islamic influences, and interactions with various neighboring civilizations.
Modern Iranian culture, while rooted in its ancient Persian past, also owes much to an 8th-century renaissance that integrated Islamic principles with existing Persian artistry and scholarship. This synthesis created a distinct cultural identity that stands out within the Middle East and Asia. Its varied geography, including mountains, deserts, and coastlines, has also contributed to a diverse range of subcultures and traditions within the country itself, making it an ethnically diverse nation.
Beyond the Borders: Iran's Global Positioning
To further contextualize Iran's continental location, it's helpful to consider its global positioning. The GPS coordinates of Iran are 32.4279° N latitude and 53.688046° E longitude. These coordinates place Iran squarely in the Northern Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere, a characteristic shared by the vast majority of the Asian continent. Understanding these precise coordinates helps visualize Iran's place on the world map, confirming its Asian identity beyond any doubt.
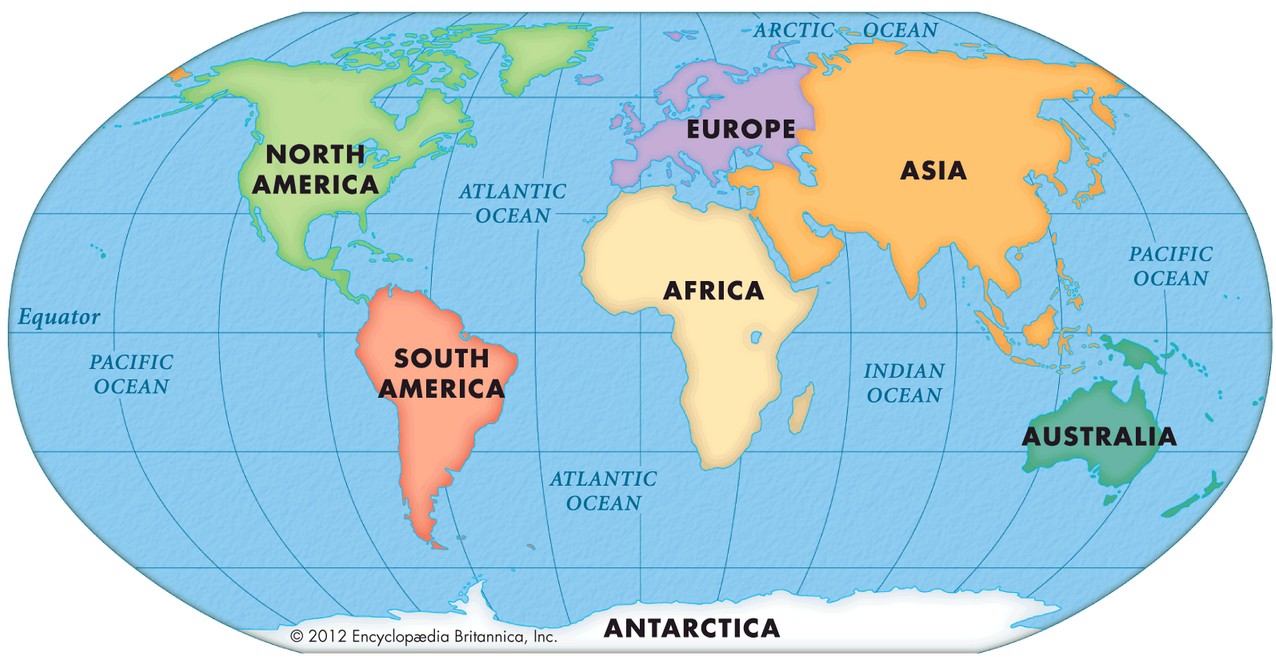
When comparing continental sizes, it's interesting to note that Asia is the largest and most populous continent. While Africa has the highest number of countries (54), followed by Europe (44), North America (23), Australia and Oceania (14), and South America (12), the sheer landmass and population of Asia are unparalleled. Iran's significant size within Asia (second largest in the Middle East) further emphasizes its prominence on the continent.
Why Understanding Iran's Continent Matters
Knowing what is the continent of Iran is not merely a matter of geographical trivia; it has significant implications for understanding global dynamics. Iran's location in Asia, specifically Western Asia, positions it at the heart of many critical geopolitical issues. Its proximity to major energy reserves, vital shipping lanes, and regions of historical conflict makes it a focal point in international relations.
Furthermore, understanding its continental context helps in appreciating its rich cultural heritage. Iran's historical interactions with other Asian civilizations, from India to China, have shaped its unique identity. Its role as an ancient imperial power and a modern nation with a significant oil industry is deeply tied to its Asian geography. For anyone studying international relations, history, or cultural studies, recognizing Iran's definitive placement within Asia is fundamental to a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal nation.
In conclusion, Iran is a country of immense historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance, firmly rooted in the Asian continent. Its position in Western Asia, bordering a multitude of nations and critical waterways, underscores its strategic importance. From its mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems to its ancient Persian legacy and vibrant modern culture, Iran is a quintessential Asian nation, contributing richly to the continent's tapestry.
Did this article clarify your understanding of Iran's continental identity? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you found this information helpful, consider sharing it with others who might be curious about Iran's unique place in the world. Explore more articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of global geography and history.
- Sunseeker Resort
- United States Involvement In Iran Iraq War
- Richest People In Iran
- Irans Dictator
- Iran And Womens Rights

Vector Map of World Bathymetry Continents | One Stop Map | World map
Carte du monde continent, la Carte du monde continent
Printable Continent Maps