Unveiling Iran's Provinces: A Journey Through Its Diverse Regions
Exploring the intricate tapestry of Iran requires a deep dive into its foundational administrative units: the Provinces of Iran. These regions, known as *ostān* in Persian, are far more than mere geographical divisions; they are vibrant centers of culture, economy, and governance, each contributing uniquely to the nation's rich heritage and modern identity. From bustling metropolises to serene natural landscapes, understanding these provinces is key to appreciating the vast diversity that defines this ancient land.
This article will guide you through the structure, significance, and unique characteristics of Iran's provinces, drawing on official data and historical context. We will uncover how these administrative divisions shape daily life, drive economic growth, and preserve the myriad traditions that flourish across the country. Prepare to embark on a fascinating journey across Iran, one province at a time.
Table of Contents
- The Administrative Backbone of Iran: Understanding Provinces
- Economic Powerhouses: Provinces and Iran's GDP
- Key Provinces: A Glimpse into Iran's Diversity
- Strategic Locations and Cultural Hubs
- Geographical Tapestry: From Coastlines to Mountains
- Demographics and Social Fabric Across Provinces
- Navigating Iran's Provinces: Codes and Maps
- The Significance of Provincial Autonomy
The Administrative Backbone of Iran: Understanding Provinces
Iran, a country with a rich history and diverse geography, is meticulously organized into administrative divisions to ensure effective governance and regional development. At the highest level of this structure are the Provinces of Iran, which serve as the primary units of regional administration. Currently, Iran is divided into 31 provinces, each with its unique identity and administrative framework.
Defining the Province (Ostān)
Each province in Iran is known as an *ostān* (Persian: استان), with the plural being *ostānhā* (استانها). The concept of an *ostān* is central to understanding Iran's internal organization. Every *ostān* is governed from a local center, which is almost always the largest and most significant local city within that province. This crucial city is designated as the capital (Persian: مرکز, *markaz*) of the province. This setup ensures that governance is centralized within the most populous and accessible urban hub, facilitating administrative functions and service delivery to the surrounding areas.
The Hierarchical Structure of Governance
The administrative divisions of Iran are arranged in a four-tiered hierarchy, ensuring a clear chain of command and localized management. The first and highest level is the province (*ostān*). Below the province, administrative authority cascades down through several more specific units:
- Counties (*Shahrestān*): Provinces are further subdivided into counties (شهرستان: *shahrestān*). These are larger geographical areas, often encompassing several towns and rural districts.
- Districts (*Bakhsh*): Each county is then divided into districts (بخش: *bakhsh*). Districts represent a more localized administrative unit, typically centered around a principal town or city.
- Rural Districts (*Dehestān*) and Cities (*Shahr*): At the most granular level, districts are composed of rural districts (دهستان: *dehestān*) and cities (شهر: *shahr*). This fine-grained division allows for highly localized governance and direct engagement with communities, whether urban or rural.
The provincial authority is headed by a governor, known as an *ostandar*. This key official is appointed by the Minister of Interior, a decision that requires the approval of the cabinet. This appointment process underscores the central government's oversight while granting the *ostandar* significant authority to manage the province's affairs, from economic development to social welfare. The capitals of the Provinces of Iran are where this local governance is primarily exercised, serving as the nerve centers for regional administration.
Economic Powerhouses: Provinces and Iran's GDP
The economic landscape of Iran is as varied as its geography, with each province contributing in distinct ways to the national economy. Analyzing the economic performance of the Provinces of Iran provides crucial insights into the country's development patterns and regional strengths.
Contribution to National Wealth (2014 Data)
Data from 2014 on the contribution of the provinces to the national GDP reveals the varying economic muscle of different regions. While specific figures for each province are not provided in the data, it's understood that certain provinces, particularly those with major industrial centers, oil and gas reserves, or significant agricultural output, play a disproportionately large role in the national economy. For instance, provinces like Tehran, Khuzestan (rich in oil), and Isfahan (known for its industries) are historically significant contributors. This distribution highlights the uneven economic development across the country, often influenced by natural resources, historical investments, and population density.
GDP Per Capita Insights (2012 Data)
Looking at the GDP per capita for the Provinces of Iran in 2012 offers a different perspective on economic well-being and productivity at the individual level. GDP per capita can indicate the standard of living and the average economic output per person in a given region. Provinces with high GDP per capita might benefit from specialized industries, high-value services, or smaller populations relative to their economic output. Conversely, lower figures could point to larger populations, reliance on less productive sectors, or underdevelopment. These economic indicators are vital for policymakers to identify areas requiring investment and support to achieve more balanced regional growth.
Key Provinces: A Glimpse into Iran's Diversity
Each of the 31 Provinces of Iran tells its own story, characterized by unique geographical features, cultural heritage, and economic activities. Let's explore some of these key provinces to understand the breadth of Iran's regional diversity.
Tehran: The Beating Heart and Capital Province
Tehran Province (استان تهران) stands as one of the 31 provinces of Iran and is arguably its most significant. Its capital is the sprawling metropolis of Tehran, which also serves as the capital city of Iran itself. Covering an area of 18,814 square kilometers (7,264 sq mi), Tehran Province is strategically located to the north of the central plateau of Iran. As the political, economic, and cultural hub of the nation, Tehran Province is home to a massive population and a vast array of industries, services, and educational institutions. Its central role makes it a crucial driver of national development and a magnet for internal migration.
Strategic Locations and Cultural Hubs
Beyond Tehran, many other Provinces of Iran hold immense strategic and cultural importance.
- Isfahan Province (استان اصفهان): Situated in the center of the country, Isfahan Province is a jewel in Iran's crown. Its capital, the city of Isfahan, is renowned globally for its stunning Islamic architecture, historical bazaars, and vibrant arts scene. The province is part of Iran's Region 2, whose secretariat is located in Isfahan, underscoring its regional administrative significance. Isfahan is not just a historical treasure but also an industrial center, contributing significantly to Iran's economy.
- Kurdistan Province (استان کردستان): Located in the west of Iran, Kurdistan Province (استان کردستان) covers an area of 28,817 km² (11,126 sq mi) and has Sanandaj as its capital. This province is part of Region 3 and shares a significant border with the Kurdistan Region of Iraq to the west. Its strategic location and unique cultural identity, shaped by its Kurdish population, make it a distinct and important part of Iran's mosaic.
- West Azerbaijan Province: Urmia, pronounced [ʔoɾˈmije], is the largest city in West Azerbaijan Province and serves as the capital of the province, the county (Urmia County), and the central district. Strategically located near the borders of Iran with Turkey and Iraq, Urmia is a significant trade and cultural hub in the northwest.
- Khuzestan Province: Ahvaz, pronounced [ʔæhˈvɒːz], is the capital of Khuzestan Province. This city and province are notable for being home to a diverse population, including Persians, Arabs, Qashqai, and Kurds, reflecting the rich ethnic tapestry of Iran. Khuzestan is also a major oil-producing region, making it economically vital.
- Zanjan Province: The city of Zanjan, pronounced [zænˈdʒɒːn], is the capital of Zanjan Province, Zanjan County, and its central district. It is known for its handicrafts, especially knives, traditional sandals, and filigree work, showcasing the unique artisanal skills of the region.
Geographical Tapestry: From Coastlines to Mountains
The geographical diversity among the Provinces of Iran is truly remarkable, ranging from arid central plateaus to lush northern forests, and from towering mountain ranges to extensive coastlines.
- Fars Province: With an area of 122,400 km², Fars Province is located in Iran's southwest and is part of Region 2. Historically significant as the heartland of the ancient Persian Empire, Fars is home to iconic sites like Persepolis. Its geography includes plains and parts of the Zagros Mountains, making it agriculturally productive and historically rich.
- Bushehr Province (استان بوشهر): Situated in the south of the country, Bushehr Province boasts a long coastline on the Persian Gulf. Its capital is the city of Bushehr. This coastal region borders Hormozgan and Fars to the southeast and east, and Khuzestan to the northwest. Inland, the region is part of the Zagros Mountains, consisting of "fingers of upland within a plateau." Bushehr is crucial for Iran's maritime trade and energy sector, hosting significant port facilities and energy infrastructure. The province was named after Hormuz, an ancient and influential trading port.
The varied topography of these provinces influences everything from climate and agriculture to population distribution and economic activities, creating a mosaic of distinct regional identities within Iran.
Demographics and Social Fabric Across Provinces
The population distribution and social characteristics of the Provinces of Iran are dynamic and multifaceted. Official census results and projections provide valuable data on the population of these provinces. Beyond mere numbers, this data often includes detailed information about a selected division's population structure, such as gender ratios, age groups, age distribution, urbanization levels, and literacy rates (for individuals aged 6 and above).
This demographic information is crucial for understanding social trends, planning public services, and addressing regional disparities. For instance, high urbanization rates in provinces like Tehran indicate significant internal migration towards urban centers, impacting infrastructure and resource allocation. Literacy rates reflect educational attainment and human capital development across different regions. The ethnic and linguistic diversity, as seen in Khuzestan with its mix of Persians, Arabs, Qashqai, and Kurds, further enriches the social fabric of the provinces, contributing to Iran's vibrant cultural landscape.
Navigating Iran's Provinces: Codes and Maps
For administrative and international identification purposes, the Provinces of Iran are assigned various codes. You'll find detailed information on Iran's provinces, including their HASC (Hierarchical Administrative Subdivision Codes), ISO (International Organization for Standardization) codes, and even domain codes. These codes are essential for data management, geographical information systems (GIS), and international referencing, providing a standardized way to identify and categorize each province.
Visual aids, such as maps, are indispensable for understanding the geographical layout of these provinces. A map showing the provinces in Iran, for example, with dimensions of 1200x1140px and a file size of 335 kb, helps visualize the boundaries and relative positions of each *ostān*. Such maps, often created by authoritative authors, provide a clear spatial representation of Iran's administrative divisions, making it easier to grasp their distribution and proximity to neighboring countries or significant geographical features.
The Significance of Provincial Autonomy
While centrally governed, the structure of the Provinces of Iran allows for a degree of localized autonomy and decision-making. The appointment of an *ostandar* by the Minister of Interior, subject to cabinet approval, ensures alignment with national policies while empowering regional leaders to address specific provincial needs. This balance is crucial for effective governance in a country as vast and diverse as Iran. Provincial capitals serve as the hubs for local governance, allowing for tailored development strategies, resource allocation, and cultural preservation efforts that reflect the unique characteristics of each region. The ability of provinces to manage their own affairs, within the broader national framework, is vital for fostering regional identity and ensuring that the diverse needs of Iran's population are met.
Conclusion
The Provinces of Iran are the fundamental building blocks of this ancient and complex nation, each contributing to its rich tapestry of culture, economy, and geography. From the bustling capital of Tehran to the coastal beauty of Bushehr and the historical depth of Fars, these administrative divisions are more than just lines on a map; they are living entities, shaped by their people, their resources, and their unique stories. Understanding the structure, governance, and individual characteristics of these provinces offers invaluable insight into the heart of Iran.
We hope this comprehensive overview has deepened your appreciation for the intricate organization and diverse nature of Iran's provinces. What fascinating facts did you learn today, or which province would you like to explore further? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or consider sharing this article with others who might be curious about Iran's unique administrative landscape. For more detailed information on specific regions or related topics, explore other articles on our site.
- Shell Energy Stadium
- Is Ice Spice Dating Anyone
- Hd Today
- Ben And Jerrys Ice Cream
- Westchester Airport
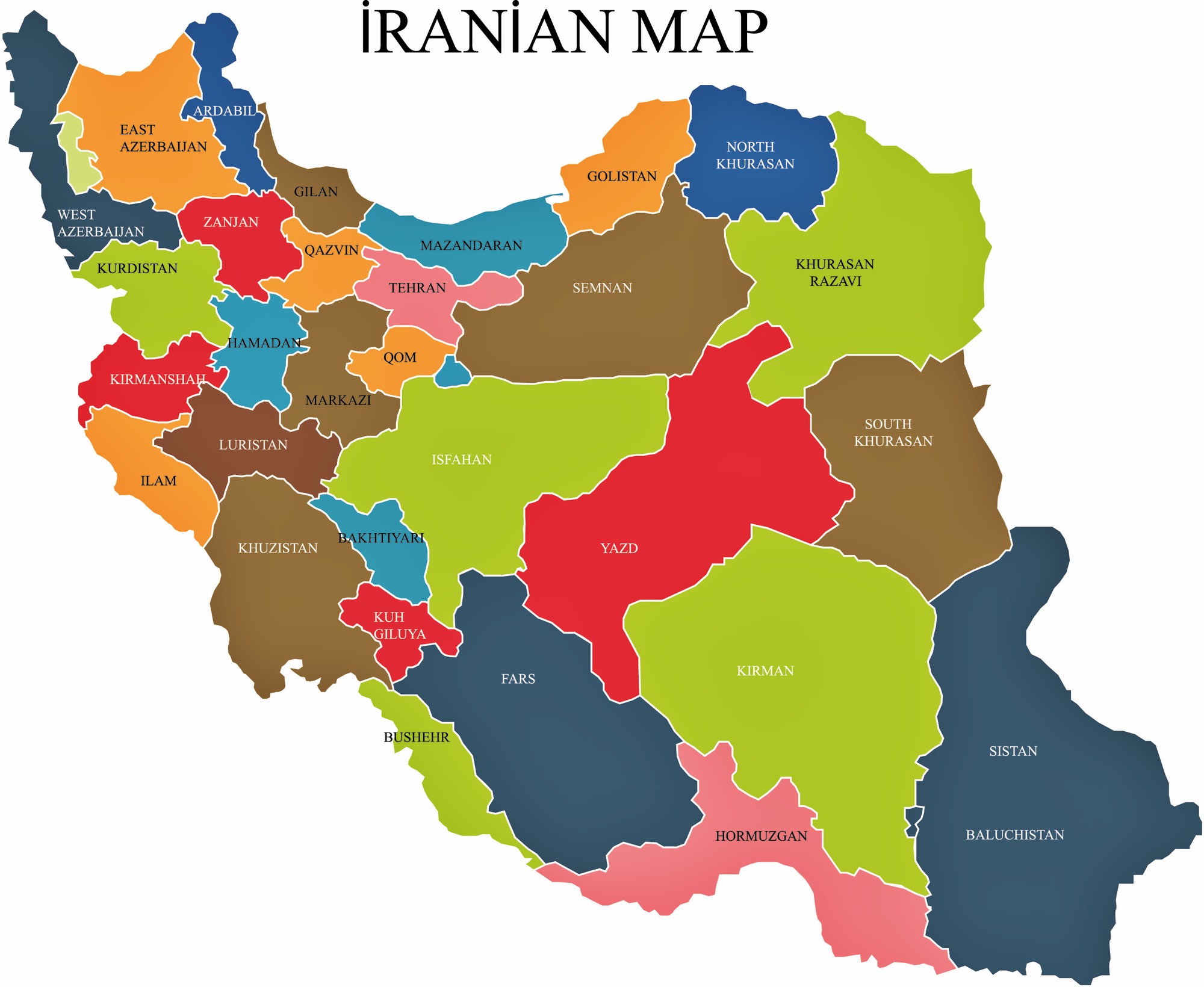
Iran Population 2024 By Province Wise Population - Neala Viviene
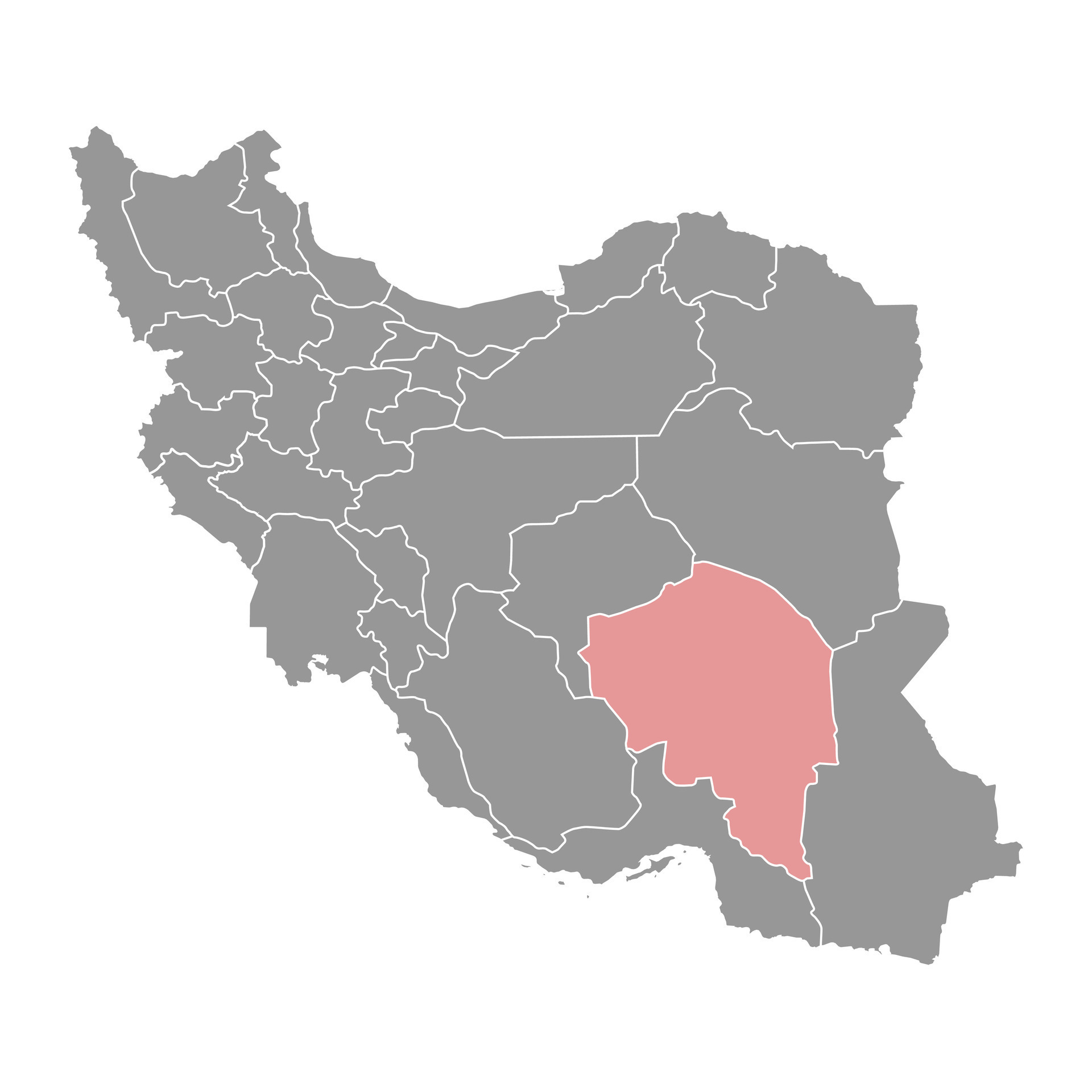
Kerman province map, administrative division of Iran. Vector
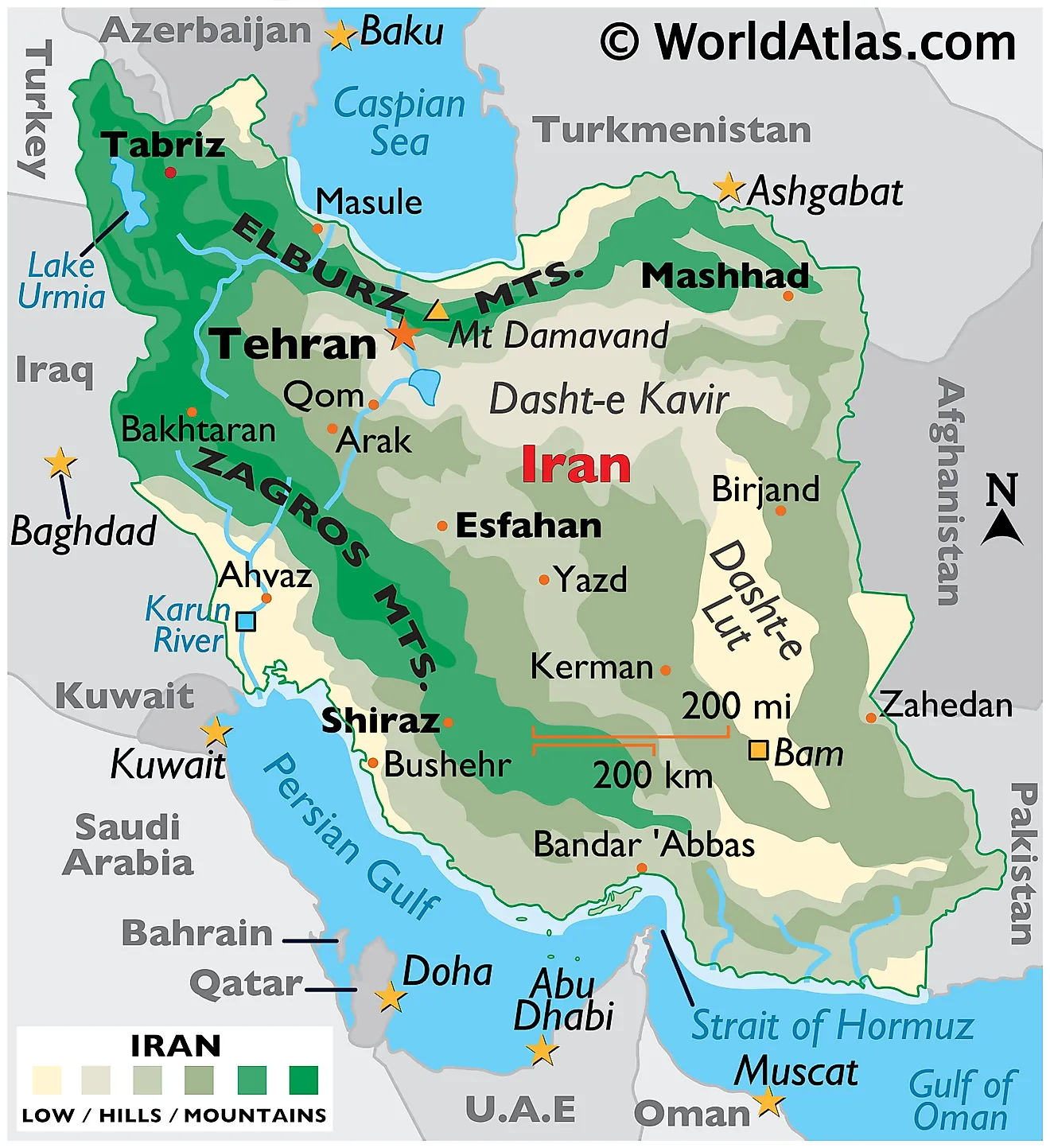
Iran Maps & Facts - World Atlas