Unveiling Tehran's Latitude: A Deep Dive Into Its Global Position
Have you ever wondered about the precise location of major cities around the world, beyond just knowing their country? For a city as historically rich and geographically diverse as Tehran, Iran, understanding its exact coordinates offers a fascinating perspective. The **latitude of Tehran, Iran** is not just a number; it's a key to unlocking insights into its climate, daily life, and strategic importance on the global map.
In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey to explore the geographical coordinates of Tehran, delving into what latitude and longitude truly mean, how they are measured, and why these seemingly simple numbers hold profound significance for the capital city of Iran. From its impact on the city's climate to its role in modern navigation and urban development, we'll uncover the multifaceted story behind Tehran's position on Earth.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Geographic Coordinates: Latitude and Longitude
- Pinpointing Tehran: The Specific Latitude
- The Significance of Tehran's Latitude: Climate and Seasons
- Tehran's Geographical Context within Iran
- Latitude's Role in Urban Planning and Development
- Exploring Tehran's Unique Position
- Verifying and Updating Geographical Data
- Beyond the Numbers: Tehran's Vibrant Life
Understanding Geographic Coordinates: Latitude and Longitude
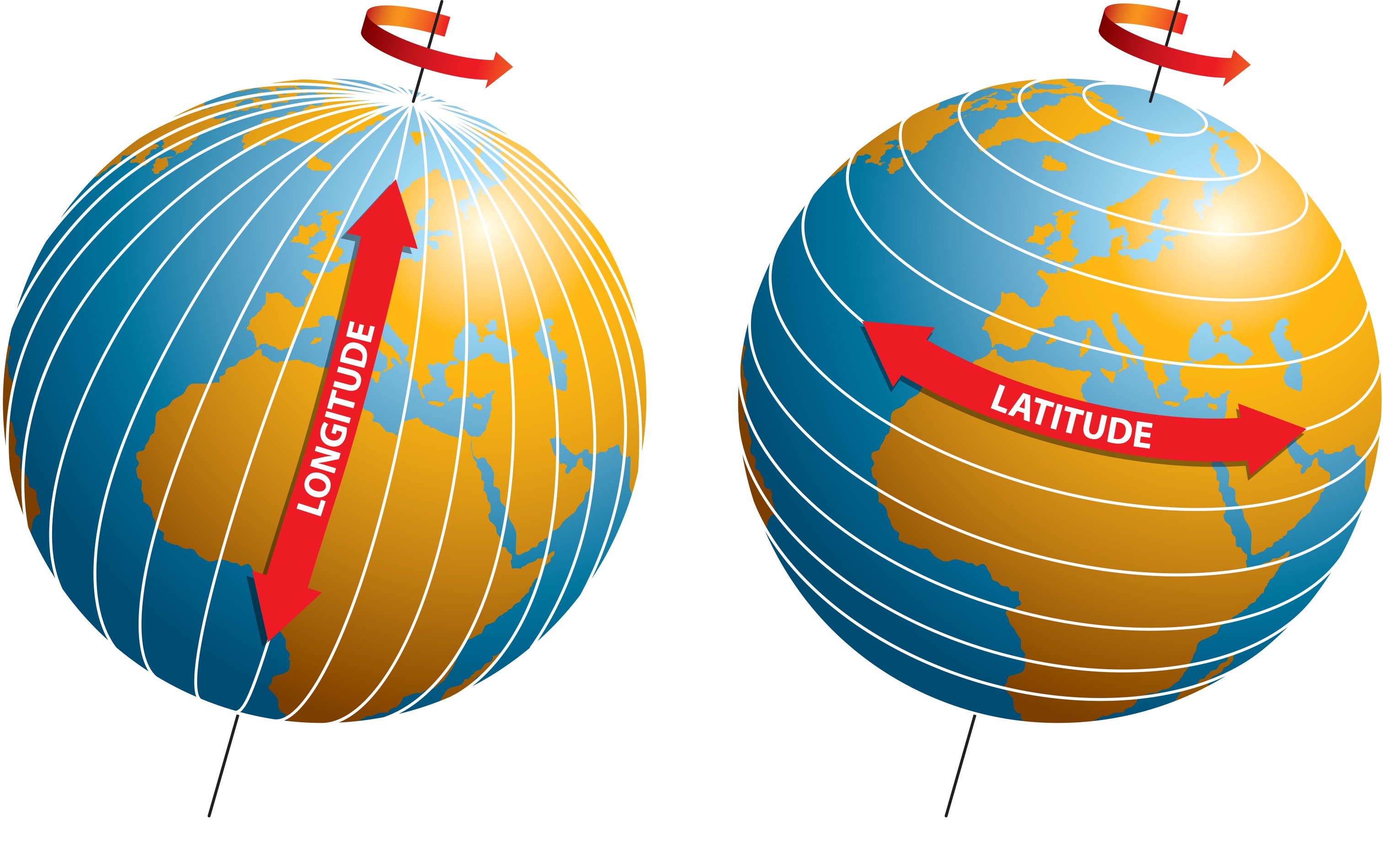
Before we pinpoint Tehran, it's essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of geographic coordinates. Geographic coordinates are a universal language for specifying any location on Earth. They use a pair of numbers – latitude and longitude – to create a unique address for every point on the globe. This system is crucial for everything from international shipping to everyday smartphone navigation.
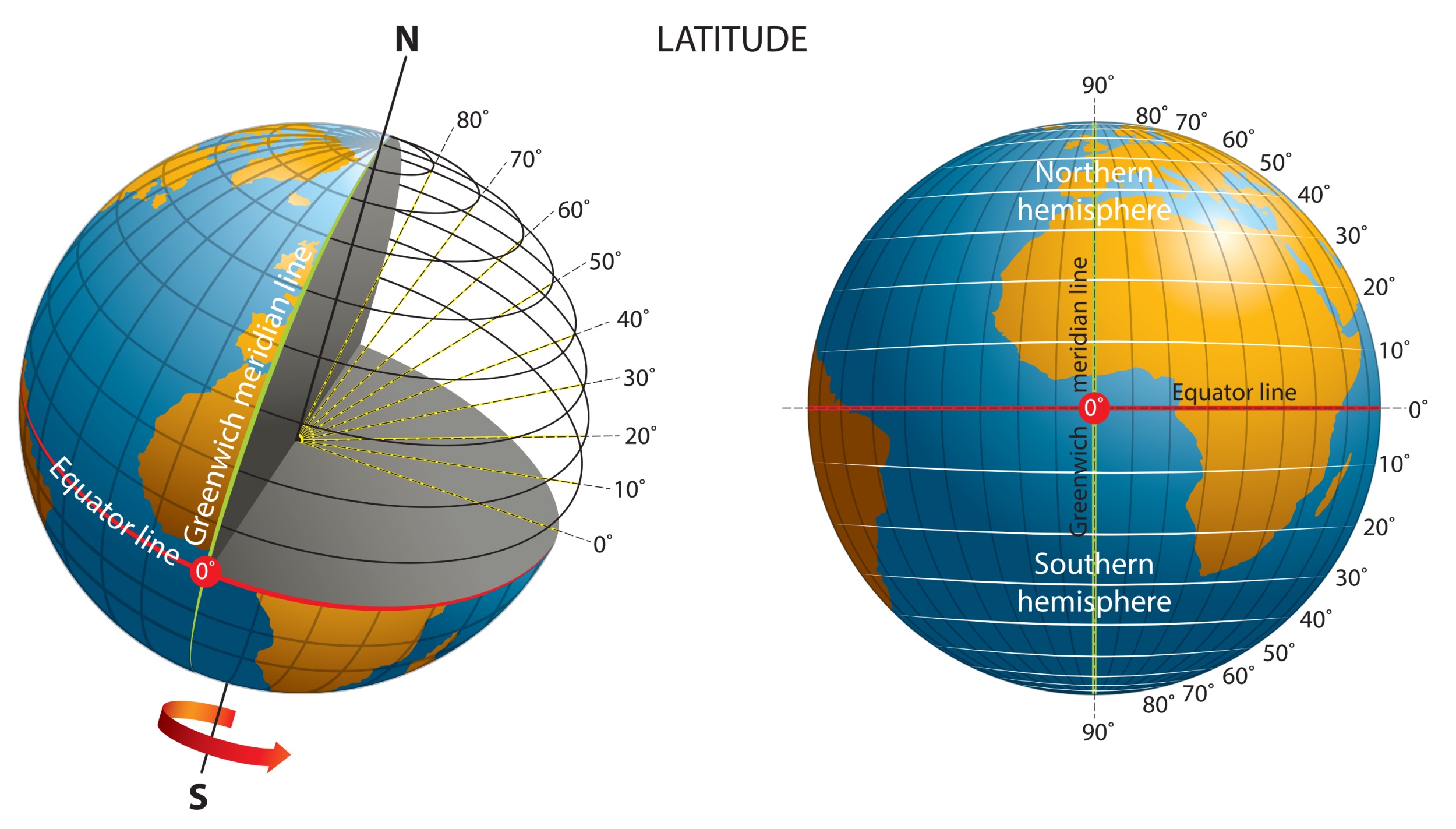
Latitude measures a location's distance north or south of the Equator. Imagine a series of imaginary circles running parallel to the Equator; these are lines of latitude. The Equator itself is 0 degrees latitude, the North Pole is 90 degrees North, and the South Pole is 90 degrees South. Values are expressed in degrees, often followed by 'N' for North or 'S' for South. For instance, the statement "The latitude and the longitude of Tehran the capital of Iran are 35° 40' S and 51° 26'E respectively" provides a specific example, though it's important to note that Tehran is in the Northern Hemisphere, so its latitude would be 'N'.
Longitude, on the other hand, measures a location's distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, an imaginary line that runs through Greenwich, London. These lines, called meridians, converge at the North and South Poles. Longitude values range from 0 to 180 degrees East or West. Together, latitude and longitude form a precise grid that allows for the exact identification of any point on Earth's surface.
Pinpointing Tehran: The Specific Latitude
Tehran, the bustling capital of Iran, is situated in the Northern Hemisphere. The provided data offers several slightly varying figures for the **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, which is common due to different measurement points within a large city, rounding, or the use of different geodetic datums. Let's look at some of these figures:
- One common reference states: "The latitude of Tehran, Iran is 35.72484160, and the longitude is 51.38165300." This is a highly precise decimal degree representation.
- Another states: "Tehran is located at Iran country in the cities place category with the gps coordinates of 35° 43' 29.43'' N and 51° 22' 53.951 E." This uses the Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS) format.
- Further data points include: "The latitude of Tehran, Iran is 35.715298, and the longitude is 51.404343." and "Tehran is located at iran country in the cities place category with the gps coordinates of 35° 42' 55.0728'' N and 51° 24' 15.6348'' E."
- A map image shows "latitude 35.6892° N and longitude 51.3890° E."
- And "Latitude and longitude of Tehran is 35.68920 N and 51.38897 E."
- Yet another precise set of coordinates is "35.6891975, 51.3889736."
- Finally, "The latitude of Tehran, Iran is 35.69439000, and the longitude is 51.42151000," which also corresponds to "Tehran is located on the latitude of 35.69439 and longitude of 51.42151."
These figures consistently place Tehran around 35.7 degrees North latitude. This range of values represents the geographical spread of the city, which is vast, encompassing various districts, landmarks, and residential areas. When discussing the **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, it's often an average or a specific central point that is referenced.
Decimal Degrees vs. Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
The coordinates for Tehran are presented in two primary formats: decimal degrees (e.g., 35.72484160) and degrees, minutes, seconds (DMS) (e.g., 35° 43' 29.43'' N). Both represent the same location but in different notations. Decimal degrees are often preferred for computational purposes and ease of use in digital systems like GPS, while DMS is more traditional and intuitive for human understanding of angles.
- **Decimal Degrees:** A single number representing the degree and fractional part (e.g., 35.72484160° N).
- **Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS):** Divides each degree into 60 minutes ('), and each minute into 60 seconds ('') (e.g., 35° 43' 29.43'' N).
The conversion between these two formats is straightforward but requires careful calculation. For example, 35° 43' 29.43'' N translates roughly to 35 + (43/60) + (29.43/3600) degrees, which results in approximately 35.72484 degrees. This consistency across different formats reinforces the accuracy of Tehran's reported geographical position.
The WGS84 Datum Explained
Many of the provided coordinates, including those for Tehran, are calculated based on the "geodetic datum WGS84." WGS84, or World Geodetic System 1984, is a global standard for representing Earth's shape and gravity field. It's the reference system used by GPS (Global Positioning System) and is fundamental to modern cartography, geodesy, and navigation.
Using a standardized datum like WGS84 ensures that coordinates from different sources are compatible and accurately align on maps and digital systems. Without a common datum, coordinates might not perfectly match up, leading to inaccuracies in mapping and navigation. The explicit mention of WGS84 for Tehran's coordinates signifies their high level of precision and interoperability with global positioning technologies.
The Significance of Tehran's Latitude: Climate and Seasons
The **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, plays a pivotal role in shaping its climate and seasonal variations. Located at approximately 35.7 degrees North, Tehran falls within the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, though its specific climate is heavily influenced by its elevation and proximity to mountain ranges.
This mid-latitude position means Tehran experiences distinct four seasons. Summers are generally hot and dry, while winters can be cold, with occasional snowfall, especially in the northern parts of the city which are closer to the Alborz mountains. The "climatic condition of Iran is featured with sub tropic Iran weather in the coastal region of Caspian Sea and semiarid or dry in other places." Tehran, being inland and at a relatively high elevation, falls into the latter category, characterized by a semi-arid or dry climate, despite its mid-latitude position. This is a classic example of how local geography (mountains, distance from large bodies of water) can significantly modify the general climatic patterns expected for a given latitude.
The latitude also dictates the amount of daylight Tehran receives throughout the year. In summer, days are long, with the sun rising high in the sky, while in winter, days are shorter, and the sun's angle is lower. This variation in solar insolation directly impacts energy consumption, agricultural cycles, and even the daily routines of its inhabitants. The 35th parallel North is a significant line, often associated with a transition from more arid to more temperate climates as one moves poleward, and Tehran sits squarely on this transition.
Tehran's Geographical Context within Iran
Understanding the **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, also requires placing it within the broader geographical context of the country. Iran itself is a vast country, located at "latitude 32.427908 and longitude 53.688046," or more broadly, "The latitude of Iran is 32.00000000, and the longitude is 53.00000000." This indicates that Iran spans a range of latitudes, generally between the low 20s and high 30s North.
Tehran's position at approximately 35.7° N makes it relatively central within Iran's latitudinal spread, though it is located in the northern part of the country. This location is strategically significant, placing it within reasonable proximity to various climatic zones and geographical features, including the Alborz mountain range to the north and the central desert plains to the south. The city's elevation, which varies significantly across its vast area, further modifies the local climate and topography, as seen on "Topographic map of Tehran, Iran" and "Elevation, latitude and longitude of Tehran, Iran on the world topo map."
Being the capital, Tehran's central-northern location facilitates its role as a hub for transportation, communication, and administration across the diverse regions of Iran. Its latitude contributes to its temperate yet dry climate, distinct from the subtropical conditions found along the Caspian Sea coast to the north or the hotter, more arid conditions in the southern desert regions.
Latitude's Role in Urban Planning and Development
The precise **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, is not merely an academic figure; it has tangible implications for urban planning, infrastructure development, and the daily lives of its millions of residents. With a population of "7.2 million (9.1% of the total population of Iran)," Tehran is a sprawling metropolis, and its geographical coordinates are fundamental to its organization and growth.
Urban planners and engineers utilize these coordinates for everything from designing efficient public transport networks to planning residential areas and industrial zones. Knowing the exact latitude helps in calculating solar angles for building design, optimizing energy efficiency, and even determining the best locations for solar power installations. Furthermore, understanding the city's precise location is crucial for disaster preparedness, especially in a seismically active region like Iran.
Navigation and GPS Applications
In the modern world, GPS (Global Positioning System) has become indispensable, and it relies entirely on accurate geographical coordinates. "Geographic coordinates of Tehran, Iran in WGS 84 coordinate system which is a standard in cartography, geodesy, and navigation, including global positioning system (GPS)" are the backbone of navigation within the city. Whether it's a taxi driver navigating through traffic, a delivery service finding an address, or a tourist exploring landmarks, GPS systems guide them using these precise latitude and longitude values.
The ubiquity of smartphones means that millions of people in Tehran daily interact with location-based services that are powered by these coordinates. From ride-sharing apps to food delivery and emergency services, the accuracy of Tehran's latitude and longitude ensures efficient and reliable operations. The ability to precisely locate any point, down to specific streets and buildings, is a testament to the power of this coordinate system.
Mapping and Cartography
The creation of accurate maps, both physical and digital, is entirely dependent on precise latitude and longitude data. "Map of Tehran with coordinates" and "Map showing the geographic coordinates of Tehran, in Iran" are direct results of this data. Cartographers use these coordinates to plot geographical features, infrastructure, and demographic information, creating detailed representations of the city.
These maps are vital tools for urban management, environmental studies, and even historical research. They allow for the visualization of urban growth, the identification of natural features like Khojir National Park, Tehran, Iran, and the planning of future developments. The consistent use of datums like WGS84 ensures that maps produced by different agencies or at different times can be seamlessly integrated and compared, providing a comprehensive understanding of Tehran's evolving landscape.
Exploring Tehran's Unique Position
Tehran's latitude, approximately 35.7° N, places it in a unique geographical and geopolitical position. It is part of Asia and the Northern Hemisphere, sharing similar latitudinal bands with other major global cities, yet its specific local geography, including its elevation and mountainous surroundings, gives it a distinct character.
The city's position has influenced its historical development, its strategic importance as a capital, and its cultural identity. Its location near the Alborz mountains provides both challenges (like seismic activity) and opportunities (like access to mountain resorts and cleaner air in higher elevations). The "current time and date in Tehran is 2:34 am on Friday," and "Tehran is located in the time zone Iran Standard Time," further highlighting its specific placement on the global clock, which is UTC+3.5, a unique half-hour offset.
This precise geographical context is what makes Tehran a fascinating subject of study, not just for geographers but for anyone interested in how location shapes human civilization. The **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, is a fundamental piece of this complex puzzle.
Verifying and Updating Geographical Data
The provided data shows slight variations in Tehran's latitude and longitude figures. While these differences are often negligible for general purposes, they highlight the dynamic nature of geographical data. For highly precise applications, continuous verification and updates are crucial. As one of the provided statements suggests, "Help us verify the data and let us know if you see any information that needs to be changed or updated." This collaborative approach to data accuracy is essential in the age of digital mapping and real-time navigation.
Factors such as tectonic plate movement, slight shifts in measurement techniques, or the establishment of new, more precise geodetic control points can lead to minor adjustments in reported coordinates over time. For a large and rapidly developing city like Tehran, maintaining up-to-date and accurate geographical information is vital for everything from infrastructure projects to emergency response systems. This commitment to precision ensures that the "elevation, latitude and longitude of Tehran, Iran on the world topo map" remain reliable resources for all users.
Beyond the Numbers: Tehran's Vibrant Life
While the latitude and longitude provide the scientific framework for understanding Tehran's location, they only tell part of the story. Tehran is a vibrant, dynamic city, home to a rich cultural heritage, bustling markets, modern skyscrapers, and a lively population. It is a center of education, with institutions like the "public research university in Tehran, Iran known traditionally to be first choice of top ranked Iranian high school."
The coordinates "35°43′00.12″ North, longitude 51°24′00.00″ East" or the precise "35.6891975, 51.3889736" define the canvas upon which this vibrant life unfolds. They underpin the city's infrastructure, its connectivity, and its ability to function as a major global capital. From the daily commute to the planning of future urban expansions, the precise geographical location is an invisible yet omnipresent factor shaping Tehran's present and future.
Conclusion
The **latitude of Tehran, Iran**, at approximately 35.7 degrees North, is far more than just a coordinate. It is a fundamental piece of information that dictates the city's climate, influences its urban development, and plays a crucial role in modern navigation and mapping. From the precise decimal degrees to the traditional Degrees, Minutes, Seconds format, and the global standard of WGS84, these numbers provide the bedrock for understanding Tehran's place on Earth.
We've explored how this latitude impacts everything from seasonal changes to the efficiency of GPS systems and the detailed work of cartographers. Tehran's position within Iran and the broader Northern Hemisphere highlights its unique geographical identity. As a city of millions, its exact coordinates are vital for its continued growth, planning, and the daily lives of its inhabitants.
What aspects of a city's geography do you find most fascinating? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you found this deep dive into Tehran's latitude insightful, consider sharing this article with others who might be curious about the science behind global locations. Explore more articles on our site to uncover other fascinating geographical insights!
- Can Women Vote In Iran
- News War Iran
- Nishapur Iran Turquoise
- Iran Leader Khamenei
- Iran Washington Embassy
Latitude e Longitude - como foram criadas, utilização, mapas
Latitude e Longitude - como foram criadas, utilização, mapas

Latitude and longitude | Definition, Examples, Diagrams, & Facts